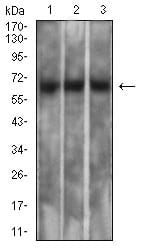
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
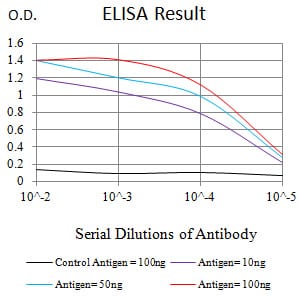
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MPF; SMRP |
| Entrez GeneID | 10232 |
| clone | 7E6A6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 69kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MSLN (AA: 296-606) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于MSLN抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Anetumab Ravtansine: A Novel Mesothelin-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate*
**作者**:Hassan R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究评估了一种靶向MSLN的抗体药物偶联物(ADC)在间皮瘤和卵巢癌中的疗效。临床前数据显示,该药物通过特异性结合MSLN阳性肿瘤细胞并释放细胞毒性药物,显著抑制肿瘤生长。I期临床试验证实其在部分患者中具有可控的安全性及初步抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**:*CAR-T Cells Engineered with a Novel Anti-MSLN scFv for Solid Tumor Therapy*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种基于抗MSLN单链抗体(scFv)的CAR-T细胞疗法。体外及小鼠模型实验表明,该疗法能有效识别并杀伤MSLN高表达的胰腺癌和肺癌细胞,同时减少对正常组织的脱靶毒性,为实体瘤治疗提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*A Bispecific Antibody Targeting MSLN and CD3 Enhances T Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Preclinical Models*
**作者**:Kachala SS, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向MSLN和T细胞表面CD3分子。实验显示,该抗体可引导T细胞特异性杀伤MSLN阳性肿瘤细胞,并在卵巢癌小鼠模型中显著缩小肿瘤体积,提示其作为免疫疗法的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*ImmunoPET Imaging of MSLN Expression Using a Novel Radiolabeled Antibody*
**作者**:Pandya D, et al.
**摘要**:研究设计了一种放射性标记的MSLN抗体用于免疫PET成像。在多种肿瘤模型和患者样本中,该探针可高灵敏度检测MSLN表达水平,为肿瘤无创诊断及治疗反应监测提供了新工具。
---
以上文献涵盖抗体药物偶联物、CAR-T细胞、双特异性抗体及影像诊断等方向,反映了MSLN抗体在肿瘤靶向治疗及检测中的多样化应用。
**Background of MSLN Antibodies**
Mesothelin (MSLN) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein encoded by the *MSLN* gene. Normally expressed at low levels in mesothelial cells lining pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum, MSLN is overexpressed in several aggressive cancers, including mesothelioma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, ovarian cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma. Its restricted normal tissue expression and tumor-associated upregulation make it a promising therapeutic target.
MSLN is implicated in tumor progression and metastasis by promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, and survival, partly through interactions with CA125/MUC16. Antibodies targeting MSLN exploit these traits for cancer therapy. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., amatuximab) block MSLN signaling or deliver cytotoxic payloads via antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs, e.g., anetumab ravtansine). Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and immunotoxins (e.g., LMB-100) also leverage MSLN’s surface accessibility to direct immune-mediated tumor killing.
Despite promise, challenges include on-target/off-tumor toxicity due to low MSLN expression in normal tissues (e.g., fallopian tubes) and tumor heterogeneity. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, combination therapies, and next-generation ADCs to enhance efficacy and safety. MSLN remains a key candidate in precision oncology, with multiple clinical trials evaluating its therapeutic potential.
×