| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
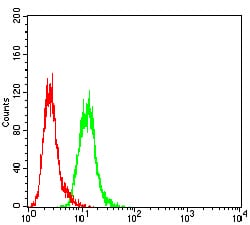
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
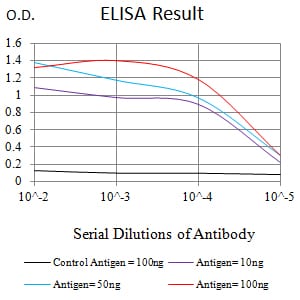
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EAC; MFT; SBS; TEM; BRSS; CDMT; MFT1; CYLD1; CYLDI; USPL2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1540 |
| clone | 5F7F4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 107.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CYLD (AA: 204-358) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CYLD抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
---
1. **《Identification of the familial cylindromatosis tumour-suppressor gene》**
- **作者**: Bignell, G.R. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过定位克隆技术鉴定了CYLD基因作为家族性圆柱瘤病的肿瘤抑制基因,发现CYLD编码一种去泛素化酶。研究中利用CYLD抗体验证了突变导致的蛋白截短,揭示了其在调控细胞增殖中的关键作用。
2. **《CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-κB activation by TNFR family members》**
- **作者**: Trompouki, E. et al.
- **摘要**: 本文发现CYLD通过去泛素化TRAF2和NEMO抑制NF-κB信号通路。研究使用CYLD抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,证明CYLD缺失导致炎症和凋亡通路异常激活。
3. **《CYLD negatively regulates cell-cycle progression by inactivating JNK1/2 and inhibiting NF-κB activity》**
- **作者**: Massoumi, R. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了CYLD通过抑制JNK和NF-κB通路调控细胞周期进程。通过CYLD抗体的免疫荧光实验,发现CYLD缺失导致细胞周期蛋白表达失调,促进肿瘤发生。
4. **《Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD regulates the peripheral development and naive phenotype maintenance of B cells》**
- **作者**: Reiley, W.W. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用CYLD缺陷小鼠和CYLD抗体分析B细胞发育,发现CYLD通过调节BAFF受体信号维持B细胞稳态,其缺失导致自身免疫反应增强。
---
以上文献均涉及CYLD抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫沉淀、免疫荧光等),并阐明CYLD在肿瘤抑制、信号通路调控及免疫细胞功能中的分子机制。
The CYLD antibody is a crucial tool in studying the cylindromatosis (CYLD) protein, a tumor suppressor encoded by the CYLD gene. Initially identified through its association with familial cylindromatosis, a condition causing benign skin tumors, CYLD functions as a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) that regulates key signaling pathways, including NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, and JNK. By removing ubiquitin chains from specific substrates, CYLD modulates inflammatory responses, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of CYLD is linked to various cancers (e.g., skin, renal, and colorectal cancers) and inflammatory disorders, underscoring its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
CYLD antibodies are widely used in research to detect CYLD expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies help elucidate CYLD's molecular interactions, post-translational modifications, and tissue-specific functions. Recent studies also explore CYLD's involvement in immune regulation, autophagy, and DNA damage repair. Commercial CYLD antibodies are typically validated for specificity and sensitivity, though variability in performance across experimental conditions necessitates careful optimization. Overall, CYLD antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling the protein's dual roles in tumor suppression and immune signaling, offering insights into therapeutic targets for CYLD-associated diseases.
×