

| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
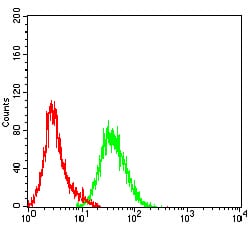
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CSF2RB; IL3RB; IL5RB; SMDP5; CDw131; betaGMR |
| Entrez GeneID | 1439 |
| clone | 8H8D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 97.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD131 (AA: extra 17-149) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD131(βc亚基)抗体相关的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Structural basis for receptor sharing by interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor*
**作者**: Carr PD et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了IL-3和GM-CSF与CD131(βc亚基)及α亚基的复合物结构,揭示了βc亚基的共享机制,为开发靶向CD131的抗体药物提供结构基础。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting the β common receptor (βc) in acute myeloid leukemia*
**作者**: Somers K et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现CD131在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中高表达,使用抗CD131单克隆抗体可阻断IL-3/GM-CSF信号通路,抑制白血病细胞增殖并促进凋亡,提示其治疗潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *A novel anti-βc antibody blocks multiple cytokine signaling and ameliorates asthma in preclinical models*
**作者**: Hercus TR et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种新型抗CD131抗体,可同时抑制IL-3、IL-5和GM-CSF的活性,在哮喘小鼠模型中显著减轻气道炎症和高反应性,为多细胞因子依赖性疾病提供治疗策略。
---
4. **文献名称**: *The βc receptor family: Structure/function insights and therapeutic potential in cancer and inflammation*
**作者**: Broughton SE et al.
**摘要**: 综述了βc(CD131)受体家族的结构特征及其在癌症和炎症中的信号调控机制,总结了靶向CD131的抗体在临床前及临床试验中的进展与挑战。
---
以上文献涵盖结构解析、疾病治疗及机制研究,均聚焦于CD131抗体的开发与应用。
CD131. also known as the β common chain (βc), is a shared subunit of receptors for interleukin-3 (IL-3), interleukin-5 (IL-5), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). These cytokines regulate hematopoiesis, immune cell activation, and inflammation. CD131 antibodies target this critical receptor component, which is expressed on myeloid cells, eosinophils, and certain leukemia cells. Research on CD131 antibodies stems from their potential to modulate dysregulated immune responses in diseases like asthma, autoimmune disorders, and myeloid leukemias, where aberrant cytokine signaling drives pathology.
The development of CD131 antibodies has been driven by the need to block pathogenic signaling cascades. For example, in eosinophil-mediated inflammation (e.g., severe asthma), antibodies inhibiting IL-5/CD131 interaction reduce eosinophil activation. In oncology, CD131 is explored as a therapeutic target due to its overexpression in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and role in leukemia stem cell survival. Antibodies against CD131 may disrupt pro-survival signals or enable antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Current challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects on healthy hematopoietic cells and understanding receptor dimerization dynamics. Nonetheless, CD131 antibodies represent a promising tool for precision immunotherapy, with ongoing studies evaluating their efficacy alone or combined with other agents to enhance therapeutic outcomes.
×