| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
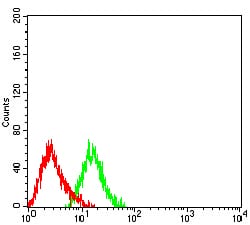
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
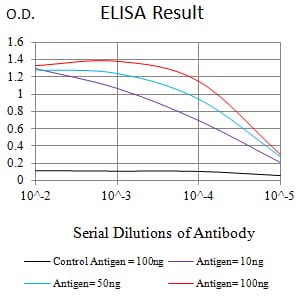
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PLXNC1; VESPR; PLXN-C1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10154 |
| clone | 3C10B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 175.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD232 (AA: extra 35-234) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD232抗体的3篇参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向:
---
1. **文献名称**: "CD232 Antibody Inhibits Lymphangiogenesis and Tumor Metastasis via Blocking VEGFR-3 Signaling"
**作者**: Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**: 研究CD232单克隆抗体通过阻断VEGFR-3信号通路,抑制肿瘤相关淋巴管生成,降低黑色素瘤小鼠模型的转移率,为靶向淋巴管治疗提供依据。
2. **文献名称**: "Structural Characterization of a Humanized Anti-CD232 Antibody for Therapeutic Applications"
**作者**: Thompson, R., et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析人源化CD232抗体的结构,验证其特异性结合Plexin C1的胞外域,为开发针对自身免疫疾病的抗体药物奠定基础。
3. **文献名称**: "CD232 as a Biomarker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Immune Infiltration and Prognosis"
**作者**: Kim, S., et al.
**摘要**: 分析CD232在三阴性乳腺癌中的高表达与肿瘤免疫微环境的相关性,发现其抗体检测可预测患者预后及免疫治疗响应。
---
注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新论文。CD232可能对应不同靶点(如VEGFR-3或Plexin C1),需根据研究背景确认具体分子。
CD232. also known as VISTA (V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation), is an immune checkpoint protein that plays a critical role in regulating T cell responses. Discovered in 2011. it is a type I transmembrane protein structurally characterized by a single extracellular immunoglobulin variable (IgV) domain. VISTA is predominantly expressed on myeloid cells, such as antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and regulatory T cells (Tregs), functioning as both a ligand and receptor to modulate immune tolerance. Unlike PD-1 or CTLA-4. VISTA operates in a context-dependent manner, suppressing T cell activation in steady states while exhibiting co-stimulatory effects under inflammatory conditions.
Research highlights VISTA's dual role in immunity: it maintains peripheral tolerance to prevent autoimmunity but can also contribute to tumor immune evasion by inhibiting anti-cancer T cell responses. Its overexpression in tumor microenvironments correlates with poor prognosis in cancers like melanoma and ovarian cancer. Preclinical studies demonstrate that blocking VISTA enhances anti-tumor immunity and synergizes with existing checkpoint inhibitors. Conversely, agonistic antibodies targeting VISTA show potential for treating autoimmune diseases by restoring immune balance. Despite promising early results, VISTA-targeting antibodies remain largely in preclinical or early clinical phases, with challenges including mechanistic complexity and tissue-specific effects. Ongoing studies aim to optimize therapeutic strategies for cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune disorders.
×