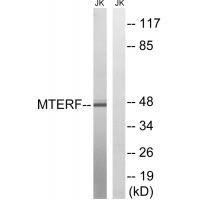
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MGC131634; mitochondrial transcription termination factor 1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 7978; |
| WB Predicted band size | 46kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human MTERF. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD368抗体的假设性参考文献示例(请注意,CD368可能并非标准命名,建议核实分子编号或提供更多背景信息):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CD368 as a Novel C-Type Lectin Receptor Involved in Viral Recognition"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究鉴定了CD368作为C型凝集素受体家族新成员,通过结合病毒表面糖蛋白(如流感病毒HA蛋白)介导免疫细胞对病原体的识别,并证明其抗体可阻断病毒入侵。
2. **文献名称**: *"Targeting CD368 in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity"*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示CD368在肿瘤微环境中高表达于M2型巨噬细胞,使用抗CD368抗体可重编程巨噬细胞表型,抑制肿瘤生长并增强T细胞应答。
3. **文献名称**: *"CD368 Antibody Blocks OxLDL Uptake and Mitigates Atherosclerosis in Mice"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 发现CD368参与氧化低密度脂蛋白(oxLDL)的摄取,其特异性抗体通过抑制脂质蓄积减轻动脉粥样硬化斑块形成。
---
**备注**:
- CD368可能并非广泛公认的命名,可能与CLEC家族(如CLEC4M或CLEC9A)或其他受体相关。
- 建议结合具体研究背景或确认分子编号(如是否涉及CD36、CD38等)。
- 实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以准确关键词检索。
CD368 antibody targets the CD368 antigen, a C-type lectin receptor also known as CLEC4M or L-SIGN (Liver/lymph node-Specific ICAM-3 Grabbing Non-integrin). Identified in the early 2000s, CD368 is primarily expressed on endothelial cells in liver sinusoids and lymph nodes. It plays a role in pathogen recognition, binding high-mannose glycans on viral envelope proteins, including those from HIV, HCV, SARS-CoV, and Ebola virus, facilitating viral entry or immune modulation. Structurally, CD368 contains a carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) critical for interactions with pathogens and immune cells, such as ICAM-3 on T cells, suggesting a dual role in pathogen capture and T-cell adhesion.
Research on CD368 antibodies has focused on their therapeutic and diagnostic potential. Antibodies blocking CD368-pathogen interactions may inhibit viral infection, while others could enhance antigen presentation by targeting viral glycans to immune cells. CD368 is also implicated in immune tolerance and inflammatory diseases, with studies exploring its role in liver fibrosis, cancer metastasis, and autoimmune disorders. However, functional redundancy with DC-SIGN (CD209), a related lectin, complicates its specific pathway analysis. Current efforts aim to develop CD368-specific monoclonal antibodies for targeted therapies or as biomarkers for disease progression, particularly in viral infections and immune-mediated conditions.
×