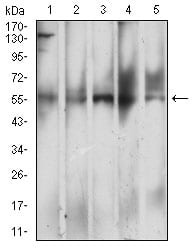
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
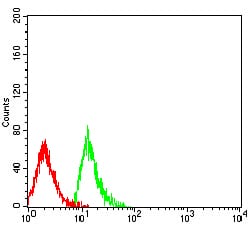
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
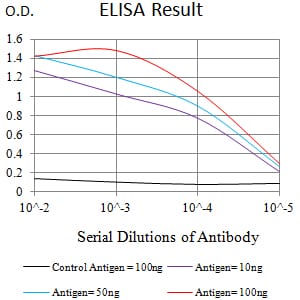
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLEC4M; LSIGN; CD209L; L-SIGN; DCSIGNR; HP10347; DC-SIGN2; DC-SIGNR |
| Entrez GeneID | 10332 |
| clone | 8A1B3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD299 (AA: extra 237-399) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD299(DC-SIGNR/L-SIGN)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **"DC-SIGNR: A novel HIV-1-binding C-type lectin that mediates trans-infection of T cells"**
- **作者**: Alvarez CP, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示了DC-SIGNR(CD299)作为C型凝集素受体在HIV-1感染中的作用,证明其通过结合病毒表面糖蛋白gp120介导病毒向T细胞的传递,并发现抗CD299抗体可阻断这一过程。
2. **"Ebola virus glycoprotein binding to DC-SIGNR: A mechanism of immune evasion?"**
- **作者**: Lozach PY, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现埃博拉病毒糖蛋白与CD299受体结合,促进病毒进入宿主细胞,并提示病毒可能通过此途径逃避免疫监测。抗CD299抗体可显著抑制病毒与宿主细胞的相互作用。
3. **"Tissue-specific regulation of immune responses by DC-SIGNR isoforms"**
- **作者**: Soilleux EJ, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过抗CD299抗体的免疫组化分析,揭示了DC-SIGNR在肝脏、淋巴结等组织的内皮细胞中高表达,并探讨其不同亚型在调节病原体识别和免疫耐受中的功能差异。
4. **"Targeting CLEC4M (DC-SIGNR) for antiviral therapy: Insights from antibody-based inhibition"**
- **作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究评估了抗CD299抗体在阻断HCV和SARS-CoV假病毒感染中的效果,证明其具有开发为广谱抗病毒药物的潜力,并分析了抗体表位与抑制效率的关系。
以上文献均聚焦于CD299在病原体感染中的生物学功能及抗体干预策略。
×