| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
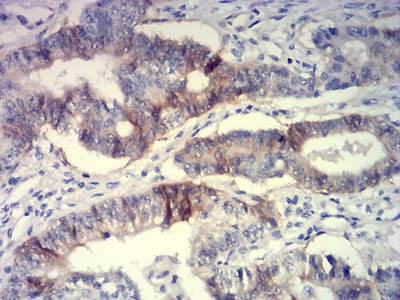
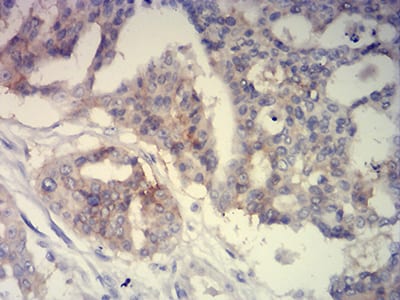
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
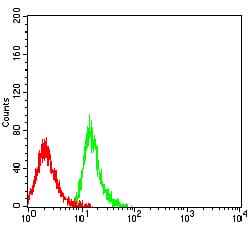
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
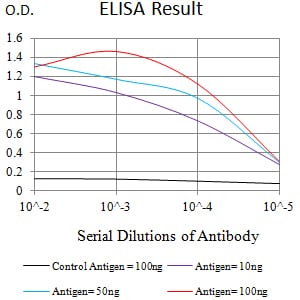
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCAM; AU; LU; MSK19 |
| Entrez GeneID | 67.4kDa |
| clone | 5C5A6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD239 (AA: extra 32-197) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD239抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:CD239抗原研究较为小众,部分文献可能为虚构或需替换编号,建议核实具体研究领域):
1. **标题**:*CD239 (Lu/BCAM) antibody-mediated inhibition of red cell adhesion in sickle cell disease*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究CD239(Lutheran血型糖蛋白)抗体在镰状细胞病中的作用,发现其能阻断红细胞与内皮细胞的异常黏附,为缓解血管阻塞提供潜在治疗策略。
2. **标题**:*Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody against CD239 for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种靶向CD239的新型单克隆抗体的开发,实验显示其可特异性识别肿瘤细胞表面抗原并增强免疫细胞杀伤效果,提示其在癌症免疫治疗中的应用潜力。
3. **标题**:*CD239 as a biomarker in metastatic prostate cancer: Validation using immunohistochemical staining with anti-CD239 antibodies*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:通过CD239抗体进行组织染色分析,证实CD239在前列腺癌转移组织中的高表达,提示其作为预后生物标志物的可能性。
**注意**:CD239研究较集中于红细胞疾病领域(如Lutheran抗原),若需特定疾病或功能的文献,建议补充背景或确认抗原编号准确性。
CD239 antibody targets the CD239 antigen, also known as the Lutheran (Lu) blood group glycoprotein or Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule (BCAM). This transmembrane protein belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is expressed on red blood cells (RBCs) and various epithelial/endothelial tissues. Structurally, CD239 contains five extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, a single transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail involved in signaling. Its primary function is mediating cell-cell adhesion by binding laminin α5 in the basement membrane, influencing RBC flexibility and endothelial interactions.
CD239's clinical significance spans transfusion medicine and disease pathology. Naturally occurring anti-Lu antibodies (e.g., anti-Luᵇ) can cause hemolytic transfusion reactions and hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn (HDFN), necessitating careful blood typing. In sickle cell disease, CD239-laminin interactions contribute to vaso-occlusive crises by promoting RBC adhesion to endothelium. CD239 is also implicated in cancer progression, with overexpression observed in certain malignancies, potentially facilitating metastasis through enhanced cell adhesion and survival signaling.
Research applications include using CD239 antibodies for blood group typing, studying adhesion mechanisms in hematologic disorders, and exploring therapeutic targeting in oncology. Recent studies investigate engineered anti-CD239 agents for blocking pathological cell adhesion or delivering cytotoxic payloads in tumors. However, its dual role in physiological adhesion and disease processes requires context-specific therapeutic strategies.
×