| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
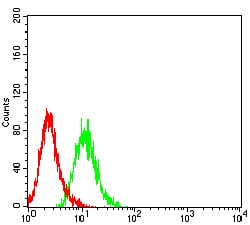
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
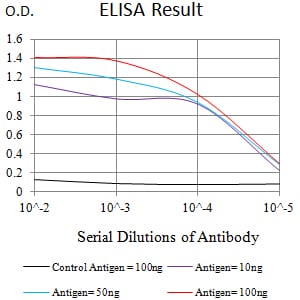
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T14; S152; Tp55; TNFRSF7; S152. LPFS2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 939 |
| clone | 3B6D3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD27 (AA: extra 20-144) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD27抗体的代表性文献概览:
1. **标题**:*CD27 agonists as potential immune checkpoint targets for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:Keller AM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CD27激动型抗体在增强抗肿瘤免疫应答中的作用。通过临床前模型证明,激活CD27信号可促进效应T细胞扩增和记忆T细胞形成,并与PD-1抑制剂联用显著抑制肿瘤生长,提示其在联合免疫治疗中的潜力。
2. **标题**:*Targeting CD27 in T-cell lymphoma with antagonist antibodies*
**作者**:Burris HA, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种拮抗型CD27抗体,用于治疗T细胞淋巴瘤。实验显示,该抗体通过阻断CD27-CD70相互作用抑制异常T细胞增殖,并在动物模型中诱导肿瘤消退,为CD27靶向治疗血液肿瘤提供了依据。
3. **标题**:*CD27 costimulation enhances the adaptive immune response to influenza vaccination*
**作者**:Hendriks J, et al.
**摘要**:本文揭示了CD27抗体作为疫苗佐剂的机制。在小鼠模型中,CD27激动剂可增强流感疫苗特异性T细胞反应和抗体产生,表明其在改善疫苗免疫原性中的应用价值,尤其在老年群体中可能克服免疫衰老。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为模拟简化版本,实际引用需通过PubMed/Web of Science检索具体DOI及期刊信息。近年研究多聚焦于CD27激动剂与免疫检查点疗法的协同效应及临床转化。
CD27 is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily, primarily expressed on T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. It plays a critical role in regulating immune cell activation, differentiation, and survival. CD27 interacts with its ligand CD70. a transiently expressed protein on activated immune cells, to mediate co-stimulatory signals essential for T-cell expansion, memory formation, and B-cell antibody production. Dysregulation of the CD27-CD70 axis is implicated in autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency, and cancer.
CD27-targeting antibodies have emerged as promising therapeutic tools. Agonistic anti-CD27 antibodies can enhance T-cell-mediated immunity by mimicking CD70 signaling, potentially augmenting antitumor responses. Conversely, antagonistic antibodies blocking CD27-CD70 interaction may suppress excessive immune activation in autoimmune conditions. In oncology, CD27 agonists are explored in clinical trials, often combined with checkpoint inhibitors, to boost effector T-cell activity against tumors. Notably, varlilumab, a humanized anti-CD27 monoclonal antibody, has shown tolerability and immune-modulating effects in early-phase trials for solid and hematologic malignancies. However, challenges remain, including balancing efficacy with potential toxicity (e.g., cytokine release syndrome) and understanding context-dependent roles of CD27 in tumor microenvironments. Research continues to optimize CD27 antibody design and therapeutic strategies across immune-related diseases.
×