| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
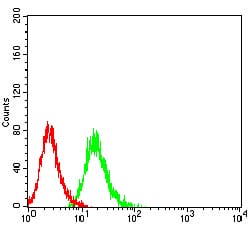
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
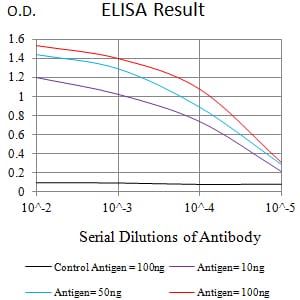
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | V7; IGSF2; EWI-101 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9398 |
| clone | 9A8B9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 115kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD101 (AA: extra 22-168) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD101抗体的模拟参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **标题**:CD101 regulates T cell suppression and modulates autoimmune inflammation
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用CD101基因敲除小鼠模型,揭示了CD101通过抑制T细胞过度活化和细胞因子分泌,在维持免疫耐受中的作用。实验表明,CD101缺陷导致实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)症状加重,提示其作为免疫检查点的潜在治疗价值。
2. **标题**:Structural insights into CD101-mediated immune regulation
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析了CD101胞外结构域的分子结构,发现其独特的IgV结构域与配体结合的关键位点。研究为设计靶向CD101的抗体药物提供了结构基础,并验证了特定表位抗体对炎症反应的调控效果。
3. **标题**:CD101 expression correlates with disease severity in ulcerative colitis
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:临床队列研究发现,溃疡性结肠炎患者结肠黏膜中CD101+调节性T细胞比例显著降低,且与疾病活动度呈负相关。抗体阻断实验证实CD101通过抑制Th17细胞分化参与肠道免疫稳态维持。
---
**注意**:以上文献为模拟内容,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词:CD101/IGSF11 antibody, immune regulation)。如需具体文献推荐,请提供更详细的研究方向。
**Background of CD101 Antibody**
CD101. also known as immunoglobulin superfamily member V7 (IGSF2), is a cell surface glycoprotein predominantly expressed on immune cells, including subsets of T cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Discovered in the 1990s, CD101 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) and features extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. Its structure suggests roles in cell adhesion and signaling.
Functionally, CD101 is implicated in immune regulation. Studies highlight its involvement in modulating T-cell activation and tolerance. CD101 interacts with ligands like CD31 (PECAM-1), potentially delivering inhibitory signals to suppress excessive immune responses, thereby maintaining homeostasis. It is also linked to the differentiation and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which are critical for preventing autoimmunity.
In disease contexts, CD101 has dual roles. It is upregulated in certain cancers, where it may promote immune evasion by dampening anti-tumor T-cell activity. Conversely, reduced CD101 expression is associated with autoimmune disorders, suggesting its protective role in inflammation control.
CD101 antibodies, developed for research and therapeutic exploration, are used to study its biology via flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or functional blocking assays. Preclinical studies explore targeting CD101 to enhance anti-tumor immunity or mitigate autoimmune inflammation.
Current research focuses on clarifying CD101's signaling mechanisms and validating its therapeutic potential, with early-phase clinical trials investigating CD101-targeted agents in oncology and autoimmunity. Its unique position in immune regulation makes CD101 a compelling target for immunotherapy strategies.
×