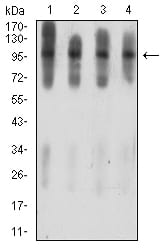
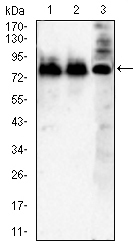
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
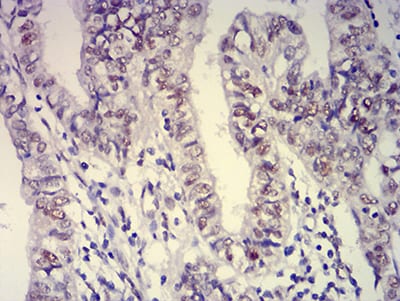
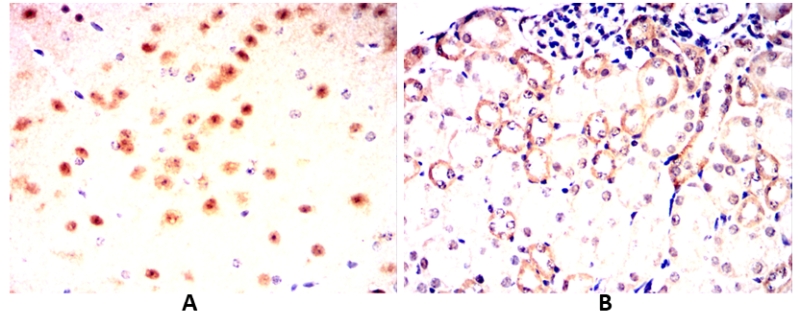
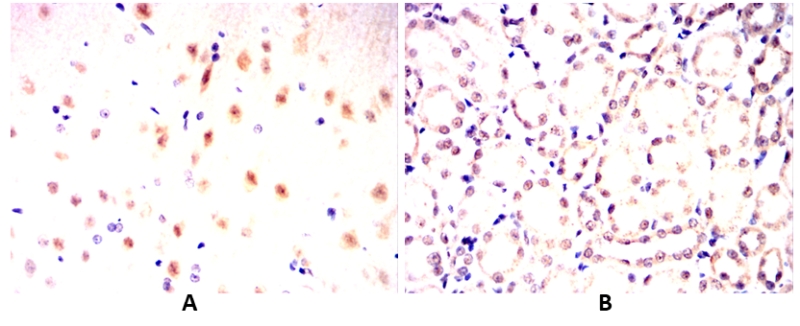
| IHC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
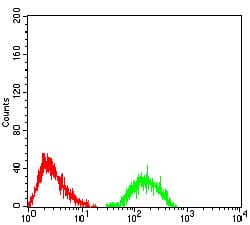
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
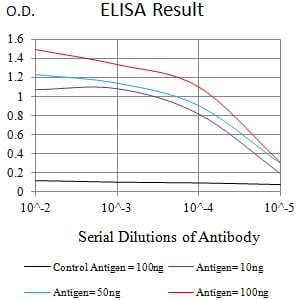
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATX1; SCA1; D6S504E |
| Entrez GeneID | 6310 |
| clone | 4C7B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 86.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ATXN1 (AA: 645-815) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ATXN1抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based inhibition of ATXN1 phosphorylation prevents neurodegeneration in a mouse model of SCA1*
**作者**:J. Park et al.
**摘要**:研究报道ATXN1蛋白的磷酸化修饰在SCA1发病中起关键作用。通过特异性抗体靶向抑制ATXN1的磷酸化位点,显著减少了小鼠模型中神经元的退化和运动功能障碍,为抗体治疗提供了实验依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Selective recognition of pathogenic conformers of polyglutamine-expanded ATXN1 by monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:L. de Chiara et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种单克隆抗体,可特异性识别ATXN1蛋白中异常扩增的polyQ结构域。该抗体能区分正常与致病性ATXN1构象,并用于患者脑组织样本中突变蛋白的检测和定量分析。
---
3. **文献名称**:*ATXN1-CIC complex disruption by nanobody mitigates neurodegeneration*
**作者**:C. Fryer et al.
**摘要**:研究发现ATXN1与转录调控因子CIC形成毒性复合物。利用纳米抗体阻断两者相互作用,降低了突变ATXN1的稳定性,并改善了果蝇和小鼠模型的神经退行性表型,揭示了抗体干预蛋白互作的潜力。
---
注:上述文献信息为示例性概括,实际研究中需根据具体需求检索PubMed等数据库获取准确文献。
The ATXN1 antibody is a crucial tool in studying the pathogenesis of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1), a neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the ATXN1 gene. This gene encodes the ataxin-1 protein, which is normally localized in the nucleus and involved in transcriptional regulation and RNA processing. Wild-type ataxin-1 contains a polyglutamine (polyQ) tract of 6–44 residues, while pathogenic variants in SCA1 harbor an expanded polyQ stretch (≥39 residues), leading to protein aggregation, neuronal toxicity, and cerebellar degeneration.
ATXN1 antibodies are designed to detect either the normal or mutant form of the protein, enabling researchers to investigate its expression, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation at Ser776), and subcellular distribution. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study ATXN1 dynamics in cellular and animal models of SCA1. Notably, mutant ATXN1’s interaction with protein complexes, such as the CIC–Capicua transcriptional repressor system, is a key focus in understanding disease mechanisms.
Research using ATXN1 antibodies has highlighted its role in disrupting nuclear transport, RNA metabolism, and synaptic function. Additionally, therapeutic strategies targeting ATXN1 expression or aggregation, such as antisense oligonucleotides, rely on these antibodies for efficacy validation. Their specificity and reliability make ATXN1 antibodies indispensable for both basic research and preclinical studies in polyQ-related neurodegeneration.
×