| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
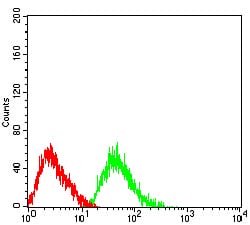
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
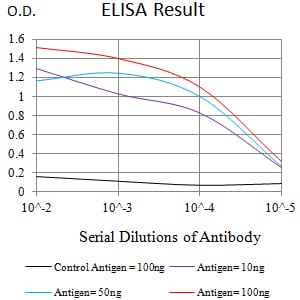
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL5RA; IL5R; CDw125; HSIL5R3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3568 |
| clone | 5E12F5D6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD125 (AA: extra 21-196) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD125(IL-5Rα)抗体的代表性文献摘要整理:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting IL-5Rα with antibody-conjugates reveals a therapeutic strategy for eosinophil-mediated diseases*
**作者**:Kolbeck R. et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种靶向CD125(IL-5Rα)的人源化抗体(如美泊利单抗前体),通过阻断IL-5信号通路显著减少嗜酸性粒细胞数量,为哮喘和嗜酸性粒细胞增多症的治疗提供了临床前依据。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of IL-5 recognition by anti-IL-5Rα monoclonal antibodies for autoimmune disease treatment*
**作者**:Li Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析CD125抗体与IL-5Rα的结合表位,揭示了抗体通过竞争性抑制IL-5与受体结合的作用机制,为优化抗体药物治疗过敏性疾病提供了结构学基础。
3. **文献名称**:*A phase II trial of anti-CD125 antibody in hypereosinophilic syndrome demonstrates reduced tissue inflammation*
**作者**:Roufosse F. et al.
**摘要**:一项II期临床试验表明,抗CD125单抗可有效降低高嗜酸性粒细胞综合征患者的血液和组织中嗜酸性粒细胞水平,并改善临床症状,证实其治疗潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*IL-5 and IL-5Rα as therapeutic targets in human diseases*
**作者**:Takatsu K. & Nakajima H.
**摘要**:综述文章系统总结了CD125抗体在哮喘、嗜酸性食管炎等疾病中的研究进展,强调其通过精准调控嗜酸性粒细胞活化通路实现靶向治疗的优势。
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究补充完整信息(年份、期刊、卷号等)。
CD125 antibody targets the alpha subunit of the interleukin-5 receptor (IL-5Rα), a key component in the IL-5 signaling pathway. IL-5 is a cytokine primarily involved in the growth, differentiation, and activation of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell critical in immune responses against parasites and in allergic inflammation. The IL-5 receptor consists of two subunits: IL-5Rα (CD125), which binds IL-5 with low affinity, and a common beta subunit (βc) shared with IL-3 and GM-CSF receptors, enabling high-affinity signaling. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in eosinophil-associated disorders, such as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, hypereosinophilic syndromes, and certain leukemias.
CD125 antibodies, typically monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), are designed to block IL-5/IL-5Rα interactions, thereby inhibiting eosinophil proliferation, survival, and tissue recruitment. Benralizumab, an FDA-approved anti-CD125 mAb, depletes eosinophils via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), showing efficacy in severe eosinophilic asthma. Research also explores CD125-targeted therapies for eosinophilic esophagitis, atopic dermatitis, and hematologic malignancies. Beyond therapeutics, CD125 antibodies serve as tools in research to study IL-5R expression and eosinophil biology. Challenges include optimizing specificity and addressing potential immunosuppressive effects. Overall, CD125 antibodies represent a strategic approach to modulate eosinophil-driven inflammation, offering targeted treatment for diseases with limited therapeutic options.
×