
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
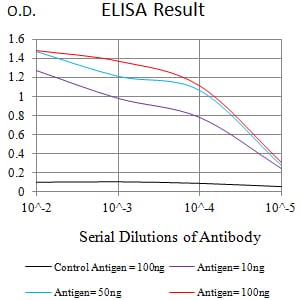
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIRPG; SIRPB2; SIRP-B2; bA77C3.1; SIRPgamma |
| Entrez GeneID | 55423 |
| clone | 4F8C10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD172G (AA: extra 29-360) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD172G(SIRPγ)抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: "SIRPγ is a novel target for antibody-based immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia"
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了CD172G(SIRPγ)在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中的高表达,并开发了一种靶向SIRPγ的单克隆抗体。实验表明,该抗体通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)显著抑制AML小鼠模型中的肿瘤生长,为AML免疫治疗提供了新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Structural and functional characterization of human SIRPγ and its interaction with CD47"
**作者**: Li et al.
**摘要**: 本研究解析了SIRPγ的晶体结构,并分析了其与CD47结合的分子机制。通过功能实验发现,靶向SIRPγ的阻断性抗体可抑制T细胞与抗原呈递细胞的相互作用,提示其在调节免疫检查点通路中的潜在应用。
---
3. **文献名称**: "CD172G identifies a subset of dendritic cells with enhanced cross-presentation capacity"
**作者**: Müller et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了CD172G抗体用于鉴定一类具有高效交叉呈递能力的树突状细胞亚群。通过流式分选和功能分析,发现此类细胞在抗肿瘤免疫应答中起关键作用,为疫苗开发提供了新靶点。
---
**备注**:CD172G(SIRPγ)是信号调节蛋白(SIRP)家族成员,主要表达于T细胞和树突状细胞,其抗体研究多聚焦于免疫调节及肿瘤治疗领域。部分文献可能使用“SIRP gamma”或“SIRPG”作为关键词。
CD172g (also known as SIRPγ or SIRPG) is a member of the signal-regulatory protein (SIRP) family, which plays roles in immune regulation and cell signaling. It shares structural homology with SIRPα (CD172a) and SIRPβ (CD172b), featuring immunoglobulin-like extracellular domains. Unlike SIRPα, CD172g lacks cytoplasmic signaling motifs, suggesting it may act as a ligand or co-receptor rather than a direct signaling molecule. It is primarily expressed on T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, where it interacts with CD47. a widely expressed "don’t eat me" signal. This interaction modulates immune cell activation, adhesion, and migration, influencing T-cell responses and immune tolerance.
CD172g has gained attention in cancer immunotherapy due to its role in regulating CD47-SIRP checkpoint pathways. Tumor cells often overexpress CD47 to evade phagocytosis, and targeting CD172g may enhance anti-tumor immunity by disrupting this axis. Antibodies against CD172g are being explored to boost T-cell activity or block immunosuppressive signals in the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, CD172g antibodies have potential applications in autoimmune diseases and transplantation by fine-tuning immune cell communication. Current research focuses on understanding its precise binding epitopes, signaling crosstalk with other immune checkpoints (e.g., PD-1), and optimizing therapeutic antibody specificity to minimize off-target effects. Its unique expression profile and mechanistic versatility make CD172g a promising but still emerging target in immunotherapeutics.
×