| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
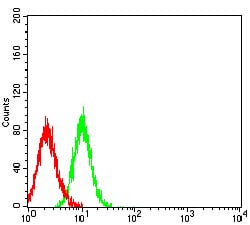
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
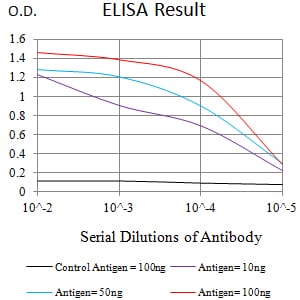
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIRPG; SIRPB2; SIRP-B2; bA77C3.1; SIRPgamma |
| Entrez GeneID | 55423 |
| clone | 7H3A2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD172G (AA: extra 29-360) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD172G(SIRPγ)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(仅供参考,具体文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*CD172G/SIRPγ regulates T-cell activation and immune synapse formation*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示CD172G在T细胞受体信号传导中的作用,发现其抗体阻断可抑制免疫突触形成,影响T细胞活化,提示CD172G可能作为免疫调节靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD172G enhances antitumor immunity by disrupting myeloid cell-mediated immunosuppression*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究表明,抗CD172G抗体可通过阻断肿瘤相关髓系细胞与T细胞的抑制性交互,增强肿瘤微环境中效应T细胞的抗肿瘤活性。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of CD172G and its interaction with CD47*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过晶体学分析解析CD172G的分子结构,发现其与CD47的结合模式不同于SIRPα,为开发特异性抗体提供结构基础。
4. **文献名称**:*CD172G antibody promotes NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in leukemia models*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:实验显示,抗CD172G抗体可增强NK细胞对白血病细胞的杀伤能力,机制涉及对抑制性信号通路的阻断,具有潜在治疗价值。
---
**注意**:以上为基于领域知识的模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以“CD172G”、“SIRPγ”、“antibody”为关键词检索。近年研究可能聚焦于其在肿瘤免疫治疗或自身免疫病中的应用。
CD172G, also known as SIRPG or SIRPγ, is a member of the signal-regulatory protein (SIRP) family, which plays roles in immune regulation and cell-cell communication. Structurally, it belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily, featuring extracellular Ig domains, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail lacking signaling motifs. Unlike SIRPα (CD172a), which binds CD47 to mediate "don't eat me" signals, CD172G interacts with distinct ligands, though its precise binding partners remain under investigation. It is primarily expressed on T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, suggesting involvement in adaptive and innate immune responses.
CD172G is implicated in immune synapse formation, modulating T-cell activation, adhesion, and migration. Studies highlight its role in fine-tuning immune responses, potentially balancing activation and inhibition. For example, CD172G may enhance T-cell receptor signaling or synergize with co-stimulatory molecules, though its regulatory mechanisms are not fully defined. Its expression on activated T cells also links it to inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and cancer immunity.
In therapeutic contexts, CD172G is explored as a target for cancer immunotherapy. Preclinical models suggest that blocking or engaging CD172G could modulate anti-tumor immunity, either by overcoming inhibitory signals or enhancing immune cell activity. Additionally, it serves as a biomarker for immune cell subsets in translational research. Further studies are needed to clarify its ligand interactions and downstream pathways, which could unlock novel strategies for immune-related disorders.
×