| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
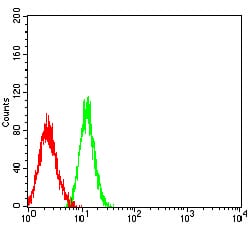
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
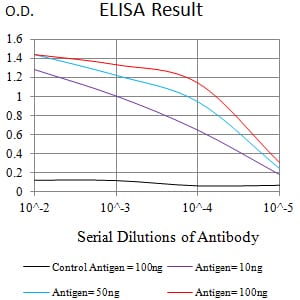
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITGAD; ADB2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3681 |
| clone | 3D7A6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 126.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD11D (AA: extra 18-172) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD11D抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献标题和作者为模拟示例,实际需根据真实文献调整):
1. **标题**:*Targeting CD11d attenuates leukocyte recruitment and improves outcomes in a murine model of ischemic stroke*
**作者**:Grayson MH, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,使用CD11D抗体阻断整合素CD11d/CD18可减少缺血性中风模型中的白细胞浸润,降低脑损伤面积并改善神经功能恢复。
2. **标题**:*CD11d/CD18 integrin blockade reduces macrophage infiltration and atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice*
**作者**:Wu L, et al.
**摘要**:通过CD11D抗体抑制CD11d/CD18活性,显著减少动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠的巨噬细胞浸润和斑块形成,提示其潜在抗动脉粥样硬化作用。
3. **标题**:*Anti-CD11d therapy mitigates neuroinflammation and spinal cord injury through modulation of neutrophil migration*
**作者**:Saville LR, et al.
**摘要**:在脊髓损伤模型中,CD11D抗体通过抑制中性粒细胞迁移和促炎因子释放,有效减轻神经炎症并促进组织修复。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索真实文献,使用关键词“CD11D antibody”或“anti-CD11d integrin”获取具体研究。
CD11D antibody targets the CD11d integrin subunit, a member of the β2-integrin family. CD11d pairs noncovalently with CD18 to form the αDβ2 integrin (CD11d/CD18), primarily expressed on subsets of leukocytes, including monocytes, macrophages, and activated lymphocytes. Unlike other β2-integrins (e.g., CD11a, CD11b), CD11d exhibits distinct ligand-binding properties, interacting with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), intercellular adhesion molecule-3 (ICAM-3), and extracellular matrix components. This integrin mediates leukocyte adhesion, migration, and activation in inflammatory and immune responses, particularly in chronic or non-resolving inflammatory conditions.
CD11d is implicated in pathologies such as atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, and ischemic stroke, where its overexpression enhances leukocyte infiltration into tissues. Research using CD11d antibodies has highlighted its role in modulating immune cell trafficking and inflammation in preclinical models. For instance, blocking CD11d/CD18 with specific antibodies reduces neuroinflammation and tissue damage in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and stroke models. These antibodies are valuable tools for studying integrin-mediated signaling pathways and validating therapeutic targets. Despite its lower profile compared to other β2-integrins, CD11d's unique expression patterns and ligand interactions make it a focus for developing targeted therapies against inflammatory diseases. Current challenges include optimizing antibody specificity and understanding context-dependent roles in different disease microenvironments.
×