| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
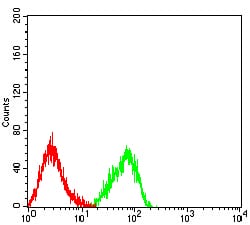
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
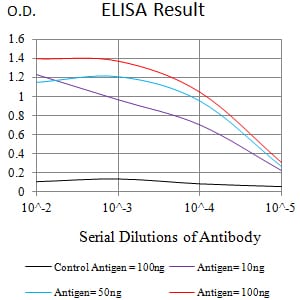
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIR2DL4; G9P; KIR103; KIR-2DL4; KIR103AS; KIR-103AS |
| Entrez GeneID | 3805 |
| clone | 2E3E12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 41.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD158D (AA: extra 22-120) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD158D抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor diversity: Balancing signals in the natural killer cell response*
**作者**: Vilches, C., & Parham, P. (2002)
**摘要**: 该综述讨论了KIR受体家族(包括CD158D)在NK细胞免疫调节中的作用,重点分析了其配体识别机制及基因多态性对疾病(如癌症、病毒感染)的影响,并提及CD158D在抑制性信号传导中的功能。
---
2. **文献名称**: *KIR2DL4 (CD158d) polymorphisms affect expression and function in NK cell-mediated IFN-γ production*
**作者**: Kikuchi-Maki, A., et al. (2003)
**摘要**: 研究通过CD158D特异性抗体实验,揭示了KIR2DL4(CD158D)在NK细胞中通过结合HLA-G诱导干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)分泌的机制,并发现其基因多态性可能导致个体间免疫应答差异。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Development of monoclonal antibodies specific for CD158d and their application in flow cytometry*
**作者**: Petersen, T., et al. (2001)
**摘要**: 本文报道了一种针对CD158D的新型单克隆抗体的开发与验证,证明其可用于流式细胞术精准检测NK细胞表面CD158D的表达水平,并验证了该抗体在功能阻断实验中的有效性。
---
4. **文献名称**: *CD158d receptor signaling in NK cells involves phosphorylation of tyrosine residues and regulates cytotoxicity*
**作者**: Rajagopalan, S., & Long, E.O. (2001)
**摘要**: 利用CD158D抗体研究其抑制性信号通路,发现受体激活后通过ITIM结构域招募磷酸酶,抑制NK细胞杀伤活性,揭示其在维持免疫耐受中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需根据具体文献调整。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“CD158D”、“KIR2DL4”等关键词检索最新研究。
The CD158D antibody targets the CD158D antigen, also known as KIR3DL4 or KIRDL4. a member of the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family. Expressed primarily on natural killer (NK) cells and subsets of T lymphocytes, KIRs regulate immune responses by interacting with human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecules. CD158D, an inhibitory receptor, contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that suppress NK cell activation upon binding to HLA-C allotypes, preventing attacks on healthy cells. This interaction is critical for maintaining immune tolerance and balancing cytotoxic activity.
CD158D's role extends to pregnancy, where it contributes to placental development by engaging HLA-G, a non-classical HLA class I molecule. Dysregulation of CD158D has been implicated in pathologies such as autoimmune disorders, viral evasion, and cancer progression. For instance, reduced HLA-C expression in tumors may diminish CD158D-mediated inhibition, potentially enhancing NK cell anti-tumor responses. Conversely, aberrant CD158D signaling may promote autoimmune tissue damage.
Antibodies against CD158D are vital tools in research and diagnostics. They enable the identification of KIR-expressing cells via flow cytometry, facilitate functional studies on NK cell regulation, and aid in exploring therapeutic strategies, such as modulating KIR-HLA interactions in immunotherapy. Additionally, CD158D's genetic diversity, driven by KIR gene polymorphisms, underscores its relevance in personalized medicine, as variations influence disease susceptibility and treatment outcomes. This antibody thus serves as a key reagent in deciphering immune regulation and developing targeted therapies.
×