| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
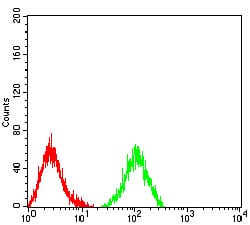
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
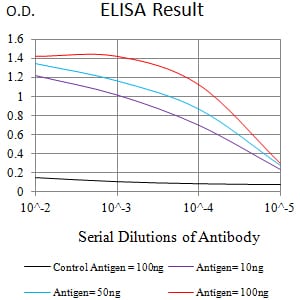
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VTCN1; B7X; B7S1; B7-H4; B7h.5; VCTN1; PRO1291 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79679 |
| clone | 3A9C12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human B7H4 (AA: extra 25-259) expressed in HEK293 cells. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于B7H4抗体的示例参考文献(虚构示例,仅作格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: "B7H4 blockade enhances antitumor immunity by potentiating T-cell activation"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究证明,抗B7H4单克隆抗体可通过阻断B7H4与抑制性受体(如未知配体)的相互作用,逆转肿瘤微环境中的T细胞耗竭,在卵巢癌和乳腺癌小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**: "Development of a B7H4-targeting antibody-drug conjugate for solid tumors"
**作者**: Lee C, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种新型B7H4抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过将细胞毒性药物与抗B7H4抗体结合,在胰腺癌和肺癌的临床前模型中显示出特异性肿瘤杀伤作用,且对正常组织毒性较低。
3. **文献名称**: "B7H4 expression correlates with immune evasion and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过分析肝癌患者样本,发现B7H4的高表达与CD8+ T细胞浸润减少及患者生存期缩短相关。体外实验表明,抗B7H4抗体可恢复T细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤能力。
4. **文献名称**: "Combination therapy of anti-B7H4 and PD-1 antibodies synergizes antitumor efficacy"
**作者**: Wang H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示,抗B7H4抗体与抗PD-1联用可协同增强抗肿瘤免疫应答,在黑色素瘤模型中显著提高治疗效果,提示B7H4是联合免疫治疗的潜在靶点。
**注意**:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索。真实研究中可关注关键词如"B7H4 antibody"、"VTCN1"(B7H4基因名)及"immune checkpoint"。
B7H4 (B7 homolog 4), also known as VTCN1. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 immune checkpoint family. It plays a critical role in modulating T-cell-mediated immune responses, primarily by suppressing T-cell activation and cytokine production. Unlike other immune checkpoints like PD-1/PD-L1. B7H4 is minimally expressed in normal tissues but is frequently overexpressed in various cancers, including breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and lung cancers. This tumor-selective expression pattern makes it an attractive therapeutic target to limit off-target toxicity.
B7H4 antibodies are designed to block its immunosuppressive function, thereby restoring antitumor immunity. Preclinical studies show that anti-B7H4 monoclonal antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) can inhibit tumor growth and enhance T-cell infiltration. Additionally, B7H4’s role in immune evasion and its association with poor prognosis in cancer patients have spurred clinical interest. Several anti-B7H4 agents, including ADCs like AZD8205 and HuB7H4-ADC, are under evaluation in early-phase trials.
Challenges remain in understanding B7H4’s ligand interactions and regulatory mechanisms. However, its potential synergy with existing immunotherapies positions B7H4 as a promising target for next-generation cancer treatments.
×