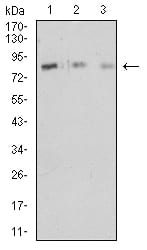
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
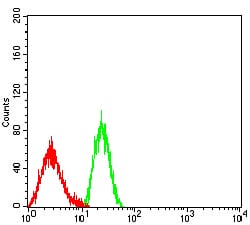
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
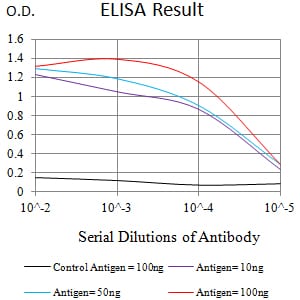
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITGB2; LAD; CD18; MF17; MFI7; LCAMB; LFA-1; MAC-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3689 |
| clone | 3D1B3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 84.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD18 (AA: extra 559-700) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD18抗体的经典文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD18 antibody reduces the severity of ischemia-reperfusion injury in a murine model*
**作者**:Kevil CG, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过在小鼠缺血再灌注模型中注射抗CD18抗体,发现其能显著减少中性粒细胞浸润和组织损伤,表明CD18介导的炎症反应是缺血损伤的关键机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CD18 integrins in leukocyte adhesion and signaling*
**作者**:Springer TA.
**摘要**:该综述系统阐述了CD18作为β2整合素亚基的功能,及其在白细胞黏附、迁移和免疫应答中的作用,为开发靶向CD18的抗体治疗炎症性疾病提供理论支持。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD18 in a rabbit model of sepsis-induced acute lung injury*
**作者**:Wilson RW, et al.
**摘要**:实验表明,使用抗CD18单克隆抗体可减少脓毒症兔模型中肺血管通透性和炎症因子释放,提示CD18阻断可能成为治疗急性肺损伤的策略。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) caused by mutations in CD18*
**作者**:Anderson DC, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过分析LAD患者基因突变,证实CD18缺陷导致白细胞无法黏附至血管内皮,强调CD18在免疫防御中的必要性,并探讨抗体干预的潜在价值。
---
这些文献涵盖了CD18的分子机制、疾病模型应用及临床相关性,可作为研究基础参考。
CD18 antibodies target the CD18 subunit of β2 integrins, a family of cell adhesion molecules critical for immune responses. CD18. encoded by the *ITGB2* gene, pairs with distinct α subunits (CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, or CD11d) to form leukocyte-specific integrins like LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). These heterodimers mediate leukocyte adhesion, migration, and signaling by binding ligands such as ICAMs, complement proteins, and fibrinogen. CD18 is essential for immune cell recruitment to inflammation sites, phagocytosis, and pathogen clearance.
CD18 antibodies are pivotal in studying leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD), a rare immunodeficiency caused by *ITGB2* mutations. Type I LAD, marked by CD18 dysfunction, leads to recurrent infections due to impaired leukocyte extravasation. In research, anti-CD18 antibodies block integrin interactions to investigate inflammatory pathways, autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), or ischemia-reperfusion injury. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against CD18 or its partners have been explored to modulate immune responses, though clinical success remains limited due to off-target effects.
These antibodies also serve as biomarkers for flow cytometry to identify immune cell subsets. Polyclonal and monoclonal variants differ in specificity: some target conserved epitopes for broad functional inhibition, while others bind unique domains for precise signaling studies. Challenges include balancing therapeutic efficacy with risks of immunosuppression. Overall, CD18 antibodies remain vital tools for dissecting integrin biology and developing immunotherapies.
×