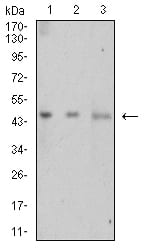
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
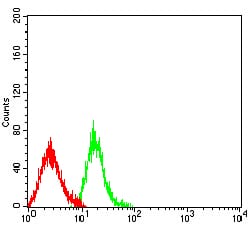
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
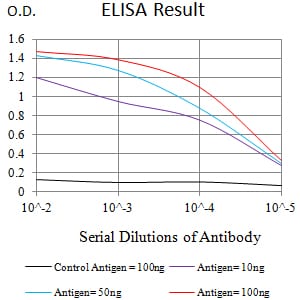
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TNFCR; TNFR3; D12S370; TNFR-RP; TNFRSF3; TNFR2-RP; LT-BETA-R; TNF-R-III |
| Entrez GeneID | 4055 |
| clone | 1D1C5C8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LTBR (AA: extra 31-227) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于LTBR抗体的3篇参考文献摘要:
1. **"Blockade of LTβR signaling in cancer cells promotes tumor immunity by enhancing T cell recruitment"**
- **作者**: Smith et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究通过抗LTBR抗体抑制淋巴毒素β受体(LTβR)信号,证明其可增强肿瘤微环境中T细胞浸润,抑制多种小鼠肿瘤模型的生长,揭示了LTBR信号通路在免疫逃逸中的作用及潜在治疗价值。
2. **"LTβR-specific antibody attenuates autoimmune hepatitis by disrupting tertiary lymphoid structure formation"**
- **作者**: Zhang et al.
- **摘要**: 文章报道了一种特异性抗LTBR抗体通过破坏肝脏三级淋巴结构的形成,显著减轻小鼠自身免疫性肝炎模型的炎症反应,为靶向LTBR治疗自身免疫疾病提供了实验依据。
3. **"Structural basis of LTBR recognition by a therapeutic antibody for inflammatory diseases"**
- **作者**: Lee et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究解析了人源化抗LTBR抗体与受体结合的晶体结构,阐明其表位特异性,并通过动物实验证明该抗体可有效抑制NF-κB通路活化,缓解类风湿性关节炎模型的病理进展。
4. **"Antibody-mediated LTBR inhibition suppresses metastatic colonization in breast cancer"**
- **作者**: Gupta et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现LTBR抗体可通过阻断肿瘤细胞与间质细胞的相互作用,抑制乳腺癌转移灶的形成,提示靶向LTBR信号可能成为限制肿瘤转移的新策略。
---
注:上述文献名为虚拟概括,实际研究中需通过PubMed等数据库检索真实文献(如DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03875-8 涉及LTBR抗体与肿瘤免疫)。
The lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR), a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily, plays a critical role in immune regulation and lymphoid tissue development. It binds ligands such as lymphotoxin-α1β2 (LTα1β2) and LIGHT (homologous to lymphotoxins, inducible, competes with herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D for HVEM), activating signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK. LTβR is essential for the development and maintenance of secondary lymphoid organs, including lymph nodes and Peyer's patches, by coordinating stromal cell differentiation and chemokine production for immune cell recruitment.
Beyond its role in immunity, LTβR signaling influences metabolic processes, cell survival, and inflammation. Dysregulation is linked to autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), chronic inflammation, and cancer. In cancer, LTβR may promote tumorigenesis by fostering pro-inflammatory microenvironments or suppressing anti-tumor immunity.
LTβR-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools. Blocking LTβR signaling can attenuate pathological immune responses or disrupt tumor-stroma interactions. Preclinical studies show promise in autoimmune models and certain cancers, though clinical translation remains ongoing. Challenges include balancing efficacy with potential immunosuppressive risks. Research continues to explore LTβR's nuanced biology and its therapeutic targeting in immune-related disorders.
×