| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
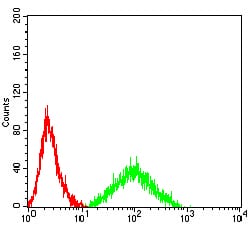
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
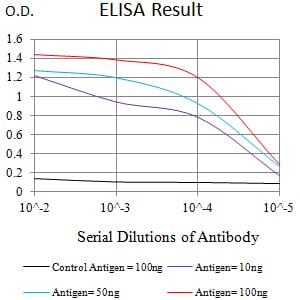
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABCB1; CLCS; MDR1; P-GP; PGY1; ABC20; GP170 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5243 |
| clone | 4G6F4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 141.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD243 (AA: 1149-1280) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD243(P-糖蛋白/MDR1)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **"Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line"**
- **作者**: Ueda K, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究首次报道了CD243(ABCB1/MDR1)在肺癌细胞中的过表达与多药耐药性的直接关联,通过抗体检测证实其膜定位及功能,为耐药机制提供了实验依据。
2. **"The role of ABC transporters in clinical practice"**
- **作者**: Gottesman MM, et al.
- **摘要**: 综述了ABC转运蛋白家族(包括CD243)在肿瘤耐药中的作用,总结了基于抗体的检测方法(如流式细胞术、免疫组化)在临床诊断和治疗评估中的应用。
3. **"Monoclonal antibodies against P-glycoprotein augment anti-leukemic efficacy of chemotherapy in AML"**
- **作者**: List AF, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究使用抗CD243单克隆抗体联合化疗治疗急性髓系白血病,发现抗体可逆转肿瘤细胞耐药性,显著提高化疗药物在体外和动物模型中的疗效。
如需具体文献来源(期刊名、卷期等),建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索上述作者和标题获取全文信息。
CD243. also known as P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), is a transmembrane efflux pump encoded by the *ABCB1* gene. It belongs to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily and plays a critical role in exporting xenobiotics, drugs, and toxins out of cells, contributing to multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancers. Overexpression of CD243 in tumor cells reduces intracellular drug accumulation, diminishing chemotherapy efficacy. This protein is also expressed in normal tissues (e.g., intestines, liver, blood-brain barrier) to protect against toxins and regulate drug absorption/metabolism.
CD243 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying P-gp expression in research and diagnostics. They are widely used in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to study MDR mechanisms, evaluate cancer prognosis, or investigate drug distribution in pharmacokinetics. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., UIC2. MRK16) target specific extracellular epitopes, enabling functional studies, while polyclonal antibodies may offer broader epitope recognition. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to homology among ABC transporters. Recent therapeutic strategies explore blocking CD243 to reverse drug resistance or leveraging its expression for targeted drug delivery.
×