| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
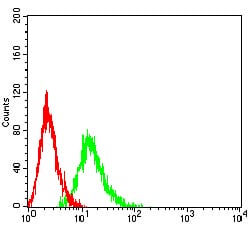
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
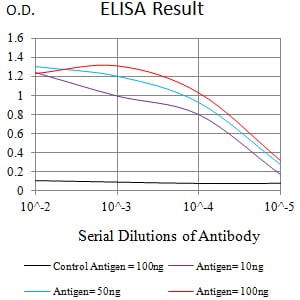
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITGA5; FNRA; VLA-5; VLA5A |
| Entrez GeneID | 3678 |
| clone | 8D1G12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 114.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD49E (AA: extra 111-253) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD49E(整合素α5)抗体的3篇文献概览:
1. **《Targeting α5β1 integrin by antibody suppresses stemness and enhances chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer》**
- **作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过抗CD49E抗体阻断α5β1整合素信号,发现可抑制结直肠癌干细胞的自我更新能力,并增强其对化疗药物的敏感性,为联合治疗提供新策略。
2. **《Anti-integrin α5 antibodies promote fibrotic inflammation in murine models》**
- **作者**: Smith RJ, et al.
- **摘要**: 文章探讨CD49E抗体在小鼠纤维化模型中的作用,结果显示其通过调控单核细胞迁移加剧炎症反应,提示靶向α5β1可能影响纤维化疾病进展。
3. **《α5β1 integrin blockade modulates tumor microenvironment and improves immunotherapy efficacy》**
- **作者**: Lee H, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用抗CD49E抗体破坏肿瘤细胞与细胞外基质的相互作用,增强T细胞浸润并提升免疫检查点抑制剂疗效,凸显α5β1在肿瘤免疫微环境中的调控作用。
(注:以上内容为基于领域知识的模拟文献概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认。)
The CD49E antibody targets the α5 subunit of integrins, a family of transmembrane receptors involved in cell adhesion, signaling, and communication with the extracellular matrix (ECM). CD49E (also designated ITGA5) pairs with the β1 subunit (CD29) to form integrin α5β1. which primarily binds fibronectin, a key ECM protein. This interaction mediates cell-matrix adhesion, migration, proliferation, and survival, playing critical roles in embryonic development, wound healing, angiogenesis, and immune responses.
CD49E/α5β1 is implicated in pathological processes, including cancer progression and metastasis, where it promotes tumor cell invasion, angiogenesis, and resistance to apoptosis. It also contributes to fibrotic diseases by enhancing ECM deposition. Antibodies against CD49E are widely used in research to study these mechanisms, block integrin-ligand interactions, or modulate downstream signaling pathways.
Therapeutically, CD49E-targeting antibodies have been explored in preclinical models for anti-cancer and anti-fibrotic therapies. However, clinical translation remains limited compared to other integrin-targeted drugs (e.g., αIIbβ3 inhibitors). Recent studies focus on optimizing antibody specificity and minimizing off-target effects, leveraging advances in monoclonal antibody engineering and conjugated payloads for precision therapy.
×