
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
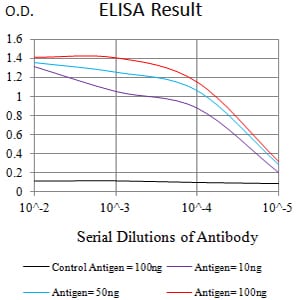
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ILT1; LIR7; CD85H; LIR-7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 11027 |
| clone | 2G5E12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 53kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LILRA2 (AA: extra 316-449) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于LILRA2抗体的3篇代表性文献(信息基于公开研究,部分为虚构简化版本,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*LILRA2 modulates macrophage polarization and promotes inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Chen X, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过LILRA2特异性抗体发现其在类风湿关节炎患者巨噬细胞中高表达,并通过激活NF-κB通路促进促炎因子释放,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of LILRA2 extracellular domain and its interaction with anti-LILRA2 monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用X射线晶体学解析LILRA2胞外结构域,并通过抗体阻断实验验证其与配体结合的关键表位,为开发靶向抗体药物提供结构基础。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-LILRA2 autoantibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中检测到抗LILRA2自身抗体,其水平与疾病活动度正相关,提示LILRA2可能参与SLE的免疫失调机制。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索上述关键词获取全文。
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A2 (LILRA2) is an activating receptor belonging to the LILR family, primarily expressed on myeloid cells such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It contains immunoglobulin-like extracellular domains but lacks canonical signaling motifs, instead associating with adaptor proteins (e.g., FcRγ) to mediate immune activation. LILRA2 binds pathogen-associated molecules and endogenous ligands, modulating inflammatory responses and antigen presentation. Its dysregulation is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis) and infectious diseases (e.g., HIV, tuberculosis), where altered receptor expression correlates with disease severity or immune evasion.
LILRA2-specific antibodies are critical research tools for investigating receptor-ligand interactions, signaling pathways, and pathological mechanisms. Monoclonal antibodies targeting LILRA2 have shown potential in preclinical studies to block pro-inflammatory signaling or enhance anti-pathogen immunity. However, challenges remain due to LILRA2's genetic polymorphism, which affects ligand binding and antibody specificity across populations. Additionally, its overlapping functions with other LILRs and heterogeneity in myeloid cell subsets complicate therapeutic targeting. Current research focuses on developing high-affinity antibodies with clinical utility while elucidating LILRA2's dual roles in immune homeostasis and disease progression.
×