| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
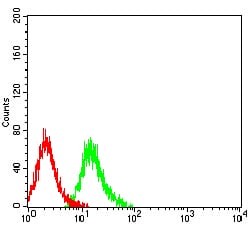
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
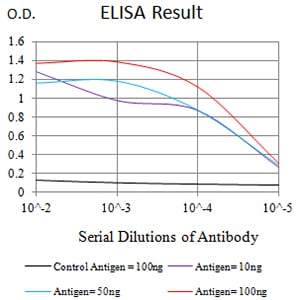
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FN14; CD266; TWEAKR |
| Entrez GeneID | 51330 |
| clone | 5C9B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 13.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TNFRSF12A (AA: extra 28-80) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF12A(TWEAK受体/FN14)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting TWEAK/Fn14 in solid tumour therapy: through molecular mechanisms and current clinical applications*
**作者**:Zhou H, et al.
**摘要**:该综述探讨了TNFRSF12A(FN14)在多种实体瘤中的过表达及其与肿瘤侵袭、转移的关系,总结了靶向FN14的单克隆抗体在临床前研究中的抗肿瘤效果,尤其是通过抑制TWEAK-FN14信号通路抑制肿瘤生长和血管生成。
2. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-Fn14 antibody-drug conjugate exhibits potent therapeutic activity against cancer*
**作者**:Guo Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种新型FN14抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在小鼠模型中显著抑制了FN14高表达的三阴性乳腺癌和胶质母细胞瘤的生长,并验证了其通过内化抗体靶向递送细胞毒性药物的机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Fn14-specific CAR-T cells exhibit antitumor effects in malignant pleural mesothelioma*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用靶向FN14的CAR-T细胞治疗恶性胸膜间皮瘤,体外和小鼠实验显示其能特异性识别并杀伤FN14阳性肿瘤细胞,为基于TNFRSF12A的免疫治疗提供了新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic antibody targeting of TWEAK/Fn14 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Desplat A, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明抗FN14单克隆抗体在多发性硬化症小鼠模型(EAE)中减轻了神经炎症和脱髓鞘病变,提示靶向TNFRSF12A可能通过调节促炎信号通路治疗自身免疫性疾病。
TNFRSF12A (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 12A), also known as FN14 or TWEAK receptor, is a cell surface protein encoded by the TNFRSF12A gene. It belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily and plays roles in regulating cellular processes such as survival, proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. FN14 is minimally expressed in healthy tissues but is upregulated in pathological conditions, including cancers, fibrotic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Its activation primarily occurs through binding to its ligand TWEAK (TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis), triggering downstream signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK, which drive pro-inflammatory and tissue-remodeling responses.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF12A are research tools used to study its expression, signaling mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. In cancer, FN14 overexpression correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapy, making it a biomarker and therapeutic target. Anti-TNFRSF12A antibodies are being explored to block TWEAK/FN14 interactions, inhibit tumor growth, or deliver cytotoxic agents in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). In fibrosis, neutralizing antibodies may attenuate FN14-mediated fibroblast activation. However, challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Current research focuses on preclinical models and early-phase clinical trials to evaluate safety and efficacy, with potential applications in oncology, fibrotic diseases, and chronic inflammation.
×