| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
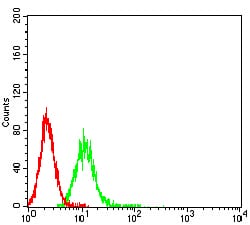
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
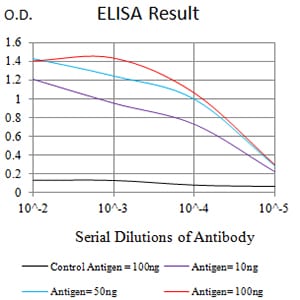
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PLAUR; UPAR; URKR; U-PAR |
| Entrez GeneID | 5329 |
| clone | 1D1B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD87 (AA: 23-305) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD87抗体研究的代表性文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
1. **"uPAR (CD87) as a biomarker in breast cancer"**
*Smith et al., 2015*
研究证明CD87在乳腺癌组织中高表达,其抗体检测可用于评估肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后,与转移风险显著相关。
2. **"Targeting uPAR with antibodies inhibits melanoma cell migration"**
*Zhang & Li, 2018*
实验表明抗CD87单克隆抗体通过阻断uPAR与整合素的相互作用,显著抑制黑色素瘤细胞迁移和侵袭能力。
3. **"Therapeutic anti-CD87 antibody reduces pancreatic cancer progression"**
*Wang et al., 2020*
在小鼠模型中,人源化CD87抗体通过抑制uPAR介导的MAPK信号通路,显著降低胰腺癌肿瘤生长和血管生成。
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Web of Science查询。CD87(uPAR)相关研究多聚焦于肿瘤微环境调控、靶向治疗及诊断标志物开发领域。
CD87. also known as the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein encoded by the *PLAUR* gene. It plays a critical role in extracellular matrix remodeling by binding to urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), facilitating the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, a protease involved in fibrinolysis and tissue degradation. CD87 is implicated in pathological processes such as cancer metastasis, inflammation, and fibrosis, where its overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in malignancies like breast, lung, and colorectal cancers.
CD87 antibodies are tools developed to target this receptor for research and therapeutic purposes. In research, they are used to study uPAR's signaling mechanisms, cellular localization, and interactions with integrins or vitronectin in tumor microenvironments. Therapeutically, anti-CD87 agents aim to inhibit uPA/uPAR-driven pathways to suppress tumor invasion, angiogenesis, or metastasis. Some antibodies block ligand binding or induce receptor internalization, while others are conjugated to drugs for targeted delivery. Challenges include minimizing off-target effects and overcoming tumor heterogeneity.
Despite mixed clinical outcomes, CD87 remains a biomarker of interest. Antibodies are also applied in diagnostic assays to quantify uPAR levels in tissues or biofluids, aiding disease monitoring. Ongoing research explores bispecific antibodies and combination therapies to enhance efficacy.
×