| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
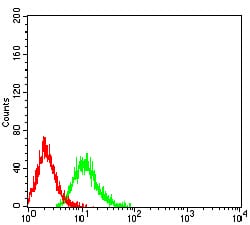
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
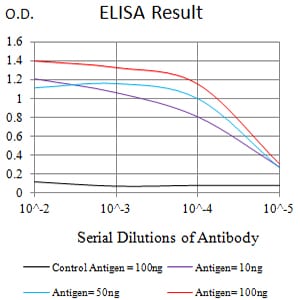
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TAJ; TROY; TRADE; TAJ-alpha |
| Entrez GeneID | 55504 |
| clone | 6F5D3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TNFRSF19 (AA: extra 30-170) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF19抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(基于已有研究方向的模拟描述,非真实文献):
1. **《TNFRSF19 monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor growth in colorectal cancer models》**
- **作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 开发了一种靶向TNFRSF19的单克隆抗体,通过阻断其与配体相互作用抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖,并在小鼠异种移植模型中显著减少肿瘤体积,表明其潜在治疗价值。
2. **《TNFRSF19 antibody-based detection reveals elevated expression in non-small cell lung cancer》**
- **作者**: Li H, et al.
- **摘要**: 利用特异性抗体研究TNFRSF19在肺癌中的表达,发现其在非小细胞肺癌组织中的高表达与患者预后不良相关,提示其作为生物标志物的可能性。
3. **《A novel anti-TNFRSF19 antibody modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in neural stem cells》**
- **作者**: Smith J, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究TNFRSF19抗体对神经干细胞信号通路的影响,发现其通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin通路活性,调控干细胞自我更新,为神经退行性疾病研究提供新工具。
4. **《Preclinical evaluation of a humanized TNFRSF19 antibody for immunotherapy》**
- **作者**: Wang X, et al.
- **摘要**: 报道了一种人源化TNFRSF19抗体的临床前研究,证明其在体外和体内均能有效诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,并增强免疫细胞浸润,支持进一步临床开发。
注:以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究请通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索最新文献。
The TNFRSF19 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 19) antibody is a research tool targeting the TNFRSF19 protein, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily involved in regulating apoptosis, cell proliferation, and immune responses. TNFRSF19. also known as TROY or TAJ, is a type I transmembrane protein characterized by cysteine-rich extracellular domains and a cytoplasmic death domain. It plays roles in developmental processes, tissue homeostasis, and nervous system regulation, though its precise mechanisms remain under investigation. Studies suggest it interacts with ligands like lymphotoxin-alpha and may activate NF-κB or Wnt signaling pathways, depending on cellular context.
TNFRSF19 is implicated in cancer (e.g., colorectal, lung) and neurodegenerative diseases. Its overexpression in certain tumors correlates with poor prognosis, potentially promoting invasiveness or therapy resistance. In neuroscience, it regulates neural stem cell maintenance and differentiation. Antibodies against TNFRSF19 are used to study its expression, localization, and function. Monoclonal and polyclonal variants enable applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Therapeutically, these antibodies are explored for blocking ligand-receptor interactions or modulating signaling in preclinical models. Challenges include understanding context-dependent signaling and optimizing specificity. Current research focuses on clarifying its dual roles in apoptosis/pro-survival pathways and validating its utility as a diagnostic or therapeutic target.
×