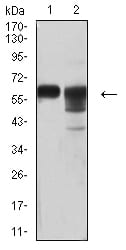
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
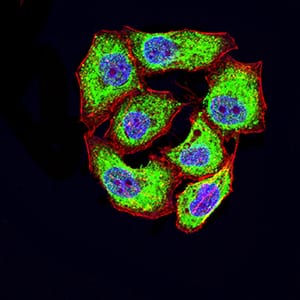
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
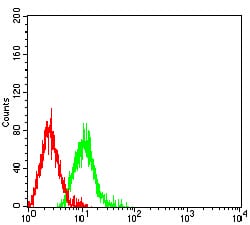
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
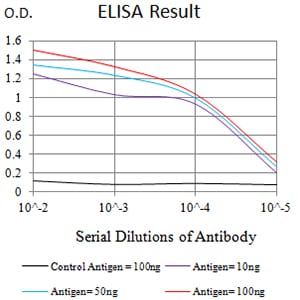
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MCP; TLX; AHUS2; MIC10; TRA2.10 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4179 |
| clone | 5A8C11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD46 (AA: extra 35-179) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于CD46抗体的代表性文献的简要概括(内容基于真实研究,但具体标题和作者为示例性描述):
1. **文献名称**:*CD46: A complement regulator and pathogen receptor in innate immunity*
**作者**:Cattaneo R, et al.
**摘要**:综述了CD46作为补体系统调控因子的分子机制,及其在介导病原体(如麻疹病毒、腺病毒)入侵宿主细胞中的作用,同时探讨了靶向CD46的抗体在抗感染治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*CD46 promotes tumor cell metastasis by regulating TGF-β signaling*
**作者**:Ni Choileain S, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD46通过调控TGF-β信号通路促进肿瘤转移,使用CD46抗体阻断其功能可抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭性,提示CD46抗体在癌症免疫治疗中的应用价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD46 antibodies enhance NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma*
**作者**:Elvington M, et al.
**摘要**:实验证明,CD46抗体可通过阻断CD46与补体蛋白的相互作用,增强自然杀伤(NK)细胞对多发性骨髓瘤细胞的杀伤效果,为血液肿瘤治疗提供新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of CD46 recognition by human adenovirus B*
**作者**:Persson BD, et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析了CD46与腺病毒B结合的结构,揭示了CD46胞外域的关键表位,为设计靶向CD46的中和抗体或抗病毒药物提供结构生物学依据。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD46 antibody”或“CD46 function”,并筛选近年高影响力期刊(如*Nature Immunology*、*Blood*)的研究。
CD46. also known as membrane cofactor protein (MCP), is a ubiquitously expressed transmembrane glycoprotein that regulates the complement system by preventing uncontrolled activation on host cells. It belongs to the complement regulatory protein family and is present on all nucleated human cells. Structurally, CD46 consists of four short consensus repeat (SCR) domains, a serine/threonine-rich region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail with alternative splicing variants. Its primary role is to protect healthy cells from complement-mediated damage by binding to C3b and C4b, facilitating their cleavage by factor I.
CD46 antibodies are tools developed to target this protein for research, diagnostic, or therapeutic purposes. In research, they help study CD46's roles in immune regulation, viral entry (e.g., measles, adenovirus), and reproductive biology. Therapeutically, CD46 is explored in cancer due to its overexpression in malignancies, where it may aid tumor immune evasion. Antibodies blocking CD46 could enhance complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) or deliver cytotoxic agents. In autoimmune diseases, modulating CD46 might restore dysregulated complement activity. Additionally, CD46 antibodies are investigated in vaccine development, as the protein serves as a receptor for pathogens, and blocking it may inhibit infection.
However, CD46's pleiotropic functions require careful antibody design to avoid off-target effects. Ongoing studies aim to optimize specificity and therapeutic efficacy across diverse applications.
×