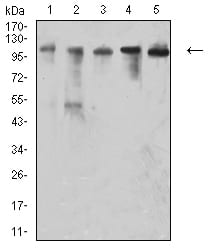
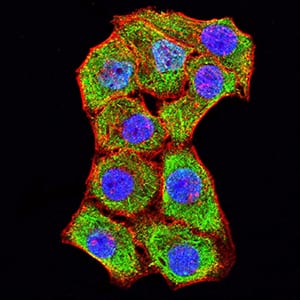
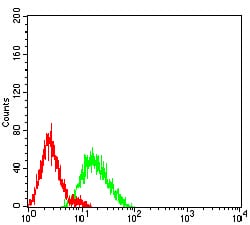
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
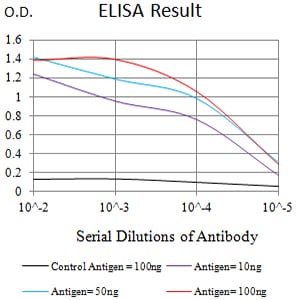
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| Aliases | VCAM1; INCAM-100 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7412 |
| clone | 6A11D8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 81.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD106 (AA: extra 25-183) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD106(VCAM-1)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting VCAM-1 with antibody-directed liposomes for imaging atherosclerosis*
**作者**:Nahrendorf M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗CD106(VCAM-1)抗体修饰的脂质体靶向活化的血管内皮细胞,实现对动脉粥样硬化斑块的分子成像。实验表明,抗体结合纳米颗粒可特异性识别并富集于病变区域,为无创诊断提供新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**:*VCAM-1-specific targeted therapy for inflammatory bowel disease*
**作者**:Briskin M, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过抗CD106抗体阻断VCAM-1与免疫细胞的相互作用,显著减轻小鼠结肠炎模型的肠道炎症反应。结果显示抗体治疗可减少中性粒细胞浸润及促炎因子释放,提示其作为IBD潜在治疗手段。
---
3. **文献名称**:*VCAM-1-mediated adhesion of hematopoietic progenitors to bone marrow stromal cells*
**作者**:Simmons PJ, et al.
**摘要**:该文献揭示了CD106在骨髓间充质干细胞表面的高表达,并通过抗体阻断实验证实其介导造血干细胞与基质细胞的黏附,对造血微环境调控及干细胞移植研究具有重要参考价值。
---
注:以上为示例性整理,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索具体研究。建议结合研究场景补充关键词(如疾病、应用方向)获取更精准文献。
CD106. also known as Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1), is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is primarily expressed on activated endothelial cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, playing a critical role in mediating leukocyte adhesion and transmigration during inflammatory responses. CD106 interacts with integrin α4β1 (VLA-4) on leukocytes, facilitating immune cell recruitment to sites of inflammation or injury. This interaction is pivotal in chronic inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer metastasis.
CD106 antibodies are valuable tools for studying endothelial activation, leukocyte-endothelial interactions, and disease mechanisms. In research, they are employed in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional blocking assays to investigate VCAM-1's role in pathologies like atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and tumor angiogenesis. Therapeutic applications are under exploration, as anti-CD106 agents may inhibit inflammatory cascades or disrupt tumor-stromal interactions. Some studies also highlight CD106's expression on mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), where it serves as a marker for immunomodulatory potency, aiding in MSC characterization for regenerative therapies. Despite its promise, CD106's pleiotropic functions necessitate context-specific evaluation in both experimental and clinical settings.
×