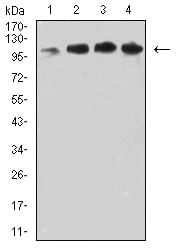
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Monkey |
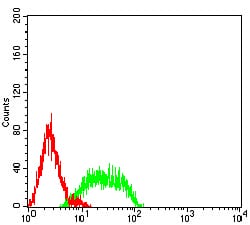
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Monkey |
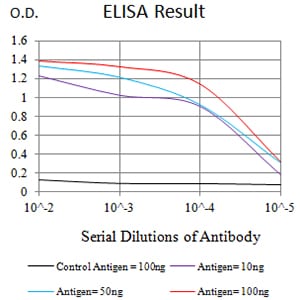
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Monkey |
| Aliases | VCAM1; INCAM-100 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7412 |
| clone | 6A11C3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 81.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD106 (AA: extra 25-183) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CD106(VCAM-1)抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) mediates lymphocyte adherence to cytokine-activated endothelium*
**作者**:Elices MJ et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次证明CD106/VCAM-1通过与整合素α4β1的相互作用,介导淋巴细胞与炎症激活的内皮细胞黏附,为炎症反应中免疫细胞迁移的机制提供了关键证据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting VCAM-1 with a monoclonal antibody for imaging inflammation in atherosclerosis*
**作者**:Kelly KA et al.
**摘要**:研究利用CD106抗体作为分子探针,通过体内成像技术检测动脉粥样硬化斑块中的炎症区域,证明其在无创诊断血管炎症中的潜在应用价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-VCAM-1 therapy reduces autoimmune disease in MRL/lpr mice*
**作者**:Kevil CG et al.
**摘要**:通过在小鼠狼疮模型中应用CD106抗体阻断VCAM-1功能,显著减轻了肾脏炎症和自身免疫损伤,提示其在治疗自身免疫性疾病中的潜力。
---
4. **文献名称**:*VCAM-1 expression in tumor vasculature promotes metastatic colonization*
**作者**:Huang J et al.
**摘要**:研究发现肿瘤血管中CD106的高表达通过促进循环肿瘤细胞黏附增强转移,靶向CD106抗体可抑制这一过程,为抗肿瘤转移治疗提供了新策略。
---
**注**:以上文献标题和作者为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体数据库(如PubMed)检索结果为准。
**Background of CD106 Antibody**
CD106. also known as Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1), is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is primarily expressed on activated endothelial cells, certain immune cells (e.g., dendritic cells), and stromal cells. CD106 mediates leukocyte-endothelial adhesion by binding to integrin α4β1 (VLA-4) on immune cells, playing a critical role in inflammation, immune response, and leukocyte trafficking.
CD106 antibodies are tools used to detect or block this molecule in research and clinical contexts. In pathological conditions, upregulated CD106 expression is associated with chronic inflammation (e.g., atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis) and cancer metastasis, where it facilitates tumor cell adhesion and extravasation. Studies using CD106 antibodies have elucidated its involvement in these processes, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. For instance, anti-CD106 strategies are explored to inhibit leukocyte infiltration in autoimmune diseases or disrupt tumor microenvironment interactions.
In experimental settings, CD106 antibodies are employed in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays (e.g., adhesion inhibition). Additionally, CD106 is a marker for certain stem cells, such as mesenchymal stromal cells, where its expression correlates with immunomodulatory properties. Overall, CD106 antibodies serve as vital reagents for investigating vascular biology, inflammation, and regenerative medicine, bridging mechanistic insights to therapeutic development.
×