| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
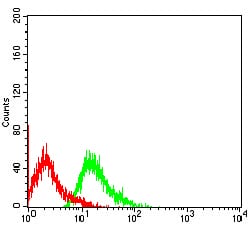
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
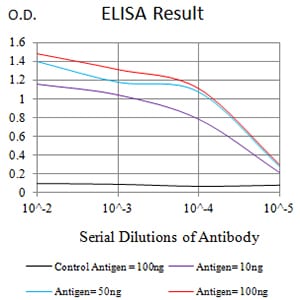
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIGLEC9; CDw329; FOAP-9; siglec-9; OBBP-LIKE |
| Entrez GeneID | 27180 |
| clone | 7G4A6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD329 (AA: extra 18–348) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD329(Siglec-9)抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Anti-Siglec-9 Antibody Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity"**
- **作者**: Zhang, Y. 等 (2022)
- **摘要**: 该研究开发了一种靶向Siglec-9(CD329)的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过抑制肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)的免疫抑制功能,增强CD8+ T细胞的抗肿瘤活性,并在小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **"Siglec-9 as a Novel Checkpoint Molecule on Myeloid Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy"**
- **作者**: Läubli, H. 等 (2020)
- **摘要**: 研究发现Siglec-9(CD329)在肿瘤浸润髓系细胞上高表达,其与唾液酸配体结合后可抑制抗肿瘤免疫反应。通过抗体阻断Siglec-9可恢复T细胞功能,为癌症免疫治疗提供新靶点。
3. **"Targeting Siglec-9 in Inflammatory Diseases: A Humanized Antibody Approach"**
- **作者**: Chen, G. 等 (2021)
- **摘要**: 该文献报道了一种人源化抗Siglec-9抗体,在炎症性疾病模型中显示可通过调节中性粒细胞和单核细胞的活化,减轻过度炎症反应,提示其在败血症或自身免疫病中的治疗潜力。
**备注**:CD329是Siglec-9的别名,主要表达于髓系免疫细胞表面,参与调控炎症和免疫抑制信号。上述研究聚焦其抗体在肿瘤免疫和炎症疾病中的应用机制。如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索标题/作者获取全文。
CD329. also known as Siglec-3 or CD33-like lectin, is a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin (Siglec) family. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and microglia. Structurally, CD329 contains an extracellular V-set immunoglobulin domain that mediates sialic acid recognition and cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) involved in signaling. Functionally, it acts as an inhibitory receptor, modulating immune responses by dampening cellular activation through ITIM-dependent recruitment of phosphatases like SHP-1/SHP-2. This regulatory role makes CD329 critical in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive inflammation.
CD329 has garnered attention in disease research, particularly in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In hematologic malignancies, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), CD329 is overexpressed on malignant cells and serves as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CD329 are explored for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or CAR-T cell therapies to eliminate cancerous cells. In Alzheimer’s disease, CD329’s involvement in neuroinflammation and microglial activation has prompted studies on its role in disease progression. Commercially available CD329 antibodies are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional studies to characterize cell populations or signaling pathways. Recent research also investigates its interactions with pathogens, including HIV-1. which may exploit CD329 for immune evasion. Despite progress, the full scope of CD329’s biological roles and therapeutic potential remains under active investigation.
×