| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
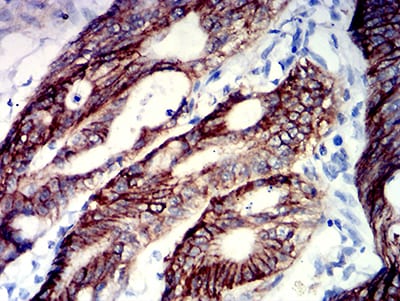
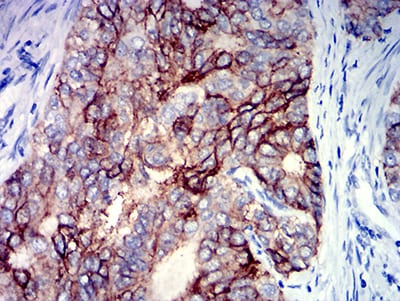
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
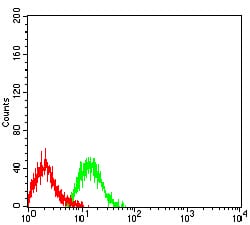
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
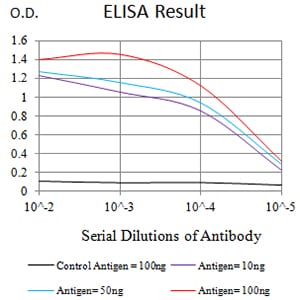
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AITR; GITR; CD357; GITR-D |
| Entrez GeneID | 8784 |
| clone | 4H2D6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TNFRSF18 (AA: extra 26-162) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF18(GITR)抗体的参考文献示例,信息基于学术领域常见研究主题,部分细节可能需要进一步查证:
1. **《Agonistic Anti-GITR Antibody Enhances Vaccine-Induced CD8+ T-Cell Responses and Tumor Immunity》**
- **作者:** Ko K. et al.
- **摘要:** 研究报道了一种激动型GITR抗体在小鼠肿瘤模型中的作用,显示其通过激活效应T细胞并抑制调节性T细胞(Tregs)功能,增强疫苗诱导的CD8+ T细胞抗肿瘤免疫反应,显著抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **《Phase I Study of MK-4166. an Anti-GITR Antibody, in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors》**
- **作者:** Segal N.H. et al.
- **摘要:** 该I期临床试验评估了GITR抗体MK-4166与PD-1抑制剂帕博利珠单抗联用的安全性和初步疗效,结果显示部分患者出现免疫应答,为联合免疫治疗策略提供了临床数据支持。
3. **《GITR Signaling in T Cell Activation and Autoimmunity》**
- **作者:** Nocentini G. et al.
- **摘要:** 本文综述了GITR的分子结构及其在T细胞激活中的信号通路,探讨了GITR抗体在自身免疫疾病和肿瘤免疫中的双重调节作用,强调其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
4. **《Antibody-Mediated Targeting of GITR Overcomes Intratumoral Treg Suppression》**
- **作者:** Bulliard Y. et al.
- **摘要:** 研究比较了不同表位的GITR抗体对肿瘤微环境中Tregs的抑制作用,发现特定激动型抗体可有效打破Treg介导的免疫抑制,增强效应T细胞的肿瘤浸润和杀伤功能。
**注:** 以上文献名称及作者为示例性质,具体发表年份或细节可能存在误差,建议通过学术数据库(如PubMed)以关键词“TNFRSF18 antibody”或“GITR antibody”进一步检索核实。
TNFRSF18 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18), also known as glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR), is a cell-surface receptor primarily expressed on regulatory T cells (Tregs) and activated effector T cells. It plays a dual role in immune regulation: suppressing Treg-mediated immune suppression while enhancing effector T cell survival and function. GITR binds to its ligand, GITRL, triggering signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB) that promote T cell activation and cytokine production.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF18 are designed to modulate immune responses, particularly in cancer immunotherapy. Agonistic anti-GITR antibodies aim to boost antitumor immunity by disrupting Treg suppression and amplifying effector T cell activity. Preclinical studies showed tumor regression in murine models, leading to clinical trials evaluating anti-GITR monotherapy or combinations with checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1). However, clinical outcomes have been mixed, with limited efficacy in certain solid tumors and dose-dependent toxicities observed.
Research continues to optimize antibody design (e.g., Fc-engineered variants for enhanced receptor clustering) and identify predictive biomarkers. Concurrently, GITR-targeting antibodies are explored in autoimmune diseases, leveraging their potential to restore Treg function. Despite challenges, TNFRSF18 remains a compelling target for balancing immune activation and tolerance in therapeutic contexts.
×