
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
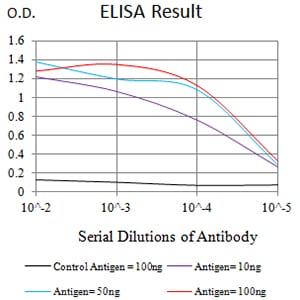
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p180; r150; CPAMD7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 135228 |
| clone | 5E11A12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 161.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD109 (AA: extra 1274-1421) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD109抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **《CD109 regulates tumorigenicity and cancer stemness via TGF-β signaling in triple-negative breast cancer》**
*作者:Li Y, et al.*
摘要:研究发现CD109在乳腺癌干细胞中高表达,通过调控TGF-β/Smad信号通路促进肿瘤干性和转移,靶向CD109的抗体可抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **《CD109 as a potential biomarker for poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma》**
*作者:Hosoya M, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫组化分析发现CD109在口腔鳞癌中过表达,其高表达与淋巴结转移和生存率降低显著相关,提示CD109抗体可作为预后标志物。
3. **《Targeting CD109 with antibody-drug conjugates in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma》**
*作者:Wang G, et al.*
摘要:开发了CD109抗体偶联药物(ADC),在皮肤鳞状细胞癌模型中显示显著抗肿瘤活性,证明CD109是新型治疗靶点。
CD109 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein belonging to the complement regulatory protein family. Initially identified as a platelet antigen, it regulates TGF-β signaling by acting as a co-receptor that modulates receptor endocytosis and downstream SMAD pathway activation. CD109 is expressed on activated T cells, endothelial cells, platelets, and certain stem cells, with roles in angiogenesis, inflammation, and tissue repair. Its overexpression is linked to cancers like squamous cell carcinoma, glioblastoma, and breast cancer, where it promotes tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance.
CD109 antibodies are critical tools for studying its function and distribution. They enable detection via flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot, aiding research on its role in TGF-β signaling crosstalk, immune regulation, and cancer biology. Some antibodies target specific epitopes or cleavage forms, such as soluble CD109 released via metalloproteinase activity. Therapeutic potential is being explored, with antibody-based strategies aiming to block CD109-mediated oncogenic pathways or enhance immune responses. However, functional diversity across cell types and disease contexts necessitates careful antibody validation to ensure specificity. Ongoing studies focus on clarifying CD109’s dual roles in homeostasis and pathology, highlighting its promise as a diagnostic or therapeutic target.
×