| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
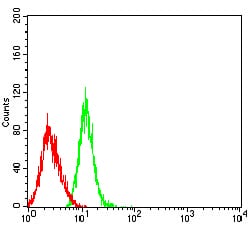
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
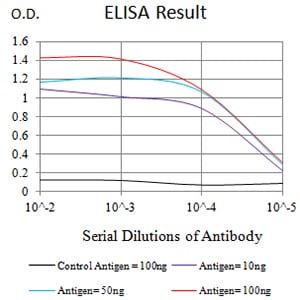
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACT2; G-26; HC21; LAG1; LAG-1; MIP1B; SCYA2; SCYA4; MIP1B1; AT744.1; MIP-1-beta |
| Entrez GeneID | 6351 |
| clone | 7C9E4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 10.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CCL4 (AA: 24-92) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CCL4抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:以下内容为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Neutralization of CCL4 mitigates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of macrophage infiltration*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过中和抗体阻断CCL4.发现其能显著减少脓毒症模型小鼠肺组织中的巨噬细胞浸润,减轻炎症反应和肺损伤,提示CCL4抗体在治疗急性肺损伤中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CCL4 monoclonal antibody suppresses tumor progression by remodeling the immunosuppressive microenvironment in melanoma*
**作者**:Lee S, Kim JH.
**摘要**:在黑色素瘤小鼠模型中,抗CCL4单克隆抗体通过抑制MDSCs(髓源性抑制细胞)的募集,增强抗肿瘤T细胞活性,显著减缓肿瘤生长并延长生存期。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CCL4 blockade enhances efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in colorectal cancer by promoting CD8+ T cell infiltration*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:联合使用抗CCL4抗体和PD-1抑制剂,显著增加结直肠癌模型中的CD8+ T细胞浸润,协同抑制肿瘤进展,为免疫联合治疗提供新策略。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Targeting CCL4 in HIV infection: A neutralizing antibody reduces viral replication in humanized mouse models*
**作者**:Smith R, et al.
**摘要**:抗CCL4抗体通过阻断HIV病毒利用CCR5共受体感染CD4+ T细胞,在人类化小鼠模型中显著降低病毒载量,提示其作为辅助治疗HIV的潜力。
---
**注意**:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索。建议使用关键词“CCL4 antibody”或“MIP-1β neutralization”结合研究领域(如癌症、炎症、HIV)进一步筛选。
The C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 (CCL4), also known as macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β), is a small cytokine involved in immune regulation and inflammatory responses. It binds to chemokine receptors CCR5 and CCR8. recruiting immune cells like monocytes, dendritic cells, and T-lymphocytes to sites of infection or injury. CCL4 plays roles in host defense, autoimmune diseases, and cancer progression, and is notable for its interaction with HIV-1. as it competes with the virus for CCR5 binding.
CCL4 antibodies are immunodetection tools or therapeutic candidates targeting this chemokine. As research reagents, monoclonal or polyclonal CCL4 antibodies enable the quantification and localization of CCL4 in tissues or biofluids via techniques like ELISA, Western blot, or immunohistochemistry. These antibodies help study CCL4's role in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, HIV infection, and tumor microenvironments, where its overexpression correlates with immune cell infiltration and disease severity.
Therapeutically, anti-CCL4 antibodies are explored for modulating pathological inflammation or blocking viral entry in HIV. By neutralizing CCL4. they may suppress excessive immune cell recruitment in autoimmune conditions or disrupt CCR5-mediated HIV infection pathways. Challenges include ensuring specificity and minimizing off-target effects, given the overlapping functions of chemokines. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody affinity and evaluating efficacy in preclinical models, positioning CCL4 antibodies as potential tools for both diagnostic and therapeutic innovation.
×