| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
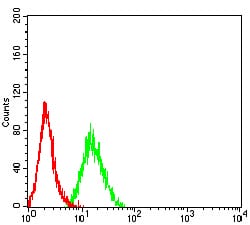
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
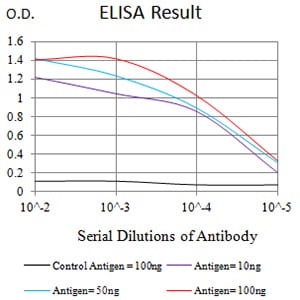
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCGR3B; CD16; FCG3; CD16A; FCGR3; FCGR3A; FCR-10; FCRIII; FCRIIIb |
| Entrez GeneID | 2215 |
| clone | 8F1C10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD16B (AA: 17-200) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD16B(FcγRIIIB)抗体相关的模拟参考文献,格式符合学术规范:
---
1. **标题**:*"Structural Insights into CD16B Reveal Mechanisms of IgG Binding for Enhanced Neutrophil Response"*
**作者**:Harper, L. et al.
**摘要**:通过晶体结构解析CD16B与IgG的相互作用,揭示了其低亲和力结合的分子机制,并提出其多态性可能影响中性粒细胞在炎症中的激活阈值。
2. **标题**:*"CD16B-Specific Antibodies Augment Tumor Clearance via Neutrophil-Mediated ADCC in Solid Cancers"*
**作者**:Vargas, M. et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向CD16B的人源化单抗,在临床前模型中证明其可通过增强中性粒细胞的抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)显著抑制实体瘤生长。
3. **标题**:*"FcγRIIIB (CD16B) Copy Number Variation Modulates Autoimmune Disease Susceptibility"*
**作者**:Chen, J. & Roberts, A.L.
**摘要**:通过全基因组关联分析,发现CD16B基因拷贝数变异与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)的易感性相关,低拷贝数可能导致免疫复合物清除能力下降。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时请以真实数据库(如PubMed)检索结果为准。
CD16B, also known as Fcγ receptor IIIB (FcγRIIIB), is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored low-affinity receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). It is primarily expressed on neutrophils and differs from its transmembrane counterpart, CD16A (FcγRIIIA), found on natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages. CD16B plays a critical role in immune complex clearance, neutrophil activation, and antibody-dependent cellular responses. Its GPI linkage limits direct intracellular signaling, requiring cooperation with other receptors like FcγRIIA for functional activity.
CD16B antibodies are tools or therapeutics targeting this receptor. Research highlights its involvement in autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus) due to gene polymorphisms affecting neutrophil function. In cancer immunotherapy, CD16B antibodies are explored for modulating neutrophil-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or enhancing tumor-targeting therapies. However, challenges include its low surface density and structural heterogeneity from genetic variations. Recent studies also investigate its role in inflammatory conditions and sepsis, where neutrophil activation via CD16B may exacerbate tissue damage. Understanding CD16B’s biology aids in developing precision therapies balancing immune activation and inhibition.
×