| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
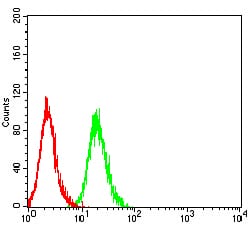
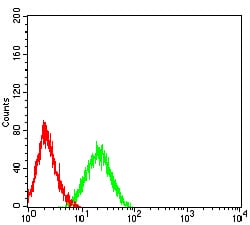
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
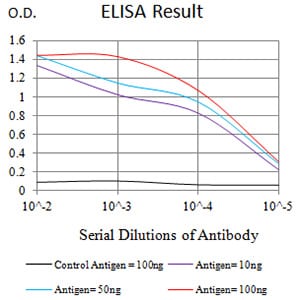
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCAR; FcalphaRI; CTB-61M7.2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2204 |
| clone | 2F9E10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD89 (AA: extra 22-227) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于CD89(FcαRI)抗体的代表性文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structure of the human IgA Fc receptor (FcαRI/CD89) in complex with IgA1-Fc*
**作者**:Carroll, K. L., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过X射线晶体学解析了CD89(FcαRI)与人IgA1-Fc的复合物结构,揭示了CD89与IgA结合的分子机制,为开发靶向该受体的抗体药物提供了结构基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD89 antibody as a novel therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid leukemia*
**作者**:Dechant, M., et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种双特异性抗体(CD89×CD33),通过结合白血病细胞表面的CD33和效应细胞(如中性粒细胞)的CD89.诱导针对急性髓系白血病(AML)的特异性杀伤作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*FcαRI (CD89) signaling controls reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and killing of fungi by human neutrophils*
**作者**:Pasquier, B., et al.
**摘要**:该研究阐明了CD89在介导中性粒细胞抗真菌免疫中的作用,发现其通过激活SHP-1磷酸酶调控ROS产生,揭示了CD89信号通路在先天免疫中的关键地位。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Neutrophil-mediated tumor cell destruction via CD64/FcγRI and CD89/FcαR*
**作者**:van Egmond, M., et al.
**摘要**:文章比较了CD89(FcαR)与CD64(FcγR)在抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)中的作用,表明CD89可通过结合IgA抗体促进中性粒细胞对肿瘤细胞的靶向清除,提示其在癌症免疫治疗中的潜力。
---
以上文献涵盖CD89的结构解析、肿瘤免疫治疗应用、信号通路机制及炎症疾病关联,可作为研究参考。如需具体期刊或年份,可进一步补充检索。
CD89. also known as FcαRI (Fc alpha receptor I), is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed primarily on myeloid cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages. It binds the Fc region of immunoglobulin A (IgA), linking innate and adaptive immunity by mediating immune responses such as phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), and inflammatory mediator release. CD89 antibodies, which target this receptor, have emerged as therapeutic tools due to their potential to modulate IgA-mediated immune activity.
In therapeutic contexts, CD89 antibodies are explored for infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancers. For example, bispecific antibodies engaging CD89 and tumor antigens redirect myeloid cells to attack malignancies, enhancing anti-cancer responses. Conversely, blocking CD89 antibodies may mitigate IgA-driven inflammation in autoimmune disorders like IgA nephropathy.
Challenges include balancing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects. Overactivation via CD89 can trigger excessive tissue damage, while inhibition may compromise mucosal immunity. Engineering efforts aim to optimize antibody formats (e.g., Fc-silenced or glyco-engineered variants) to improve specificity and safety. Preclinical studies highlight CD89's role in pathogen clearance and tumor surveillance, but clinical translation remains ongoing. Recent trials focus on CD89-targeted immunotherapies for hematologic cancers, leveraging myeloid cell engagement.
Overall, CD89 antibodies represent a versatile platform for immune modulation, though their dual roles in immunity necessitate precise therapeutic design to harness benefits while minimizing risks.
×