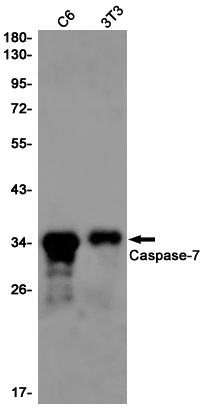
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mch3; CMH-1; mCASP-7; AI314680; ICE-IAP3; caspase-7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 12369 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of mouse Caspase-7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD89抗体(Fcα受体)的模拟参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向:
1. **文献名称**:*CD89-mediated IgA immune complex clearance in neutrophil function and inflammatory diseases*
**作者**:Jan G.J. van de Winkel 等
**摘要**:探讨CD89在中性粒细胞和单核细胞中清除IgA免疫复合物的分子机制,及其功能异常与慢性炎症疾病(如IgA肾病)的关联,提出靶向CD89可能调节过度炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD89 for tumor immunotherapy via bispecific antibody engineering*
**作者**:Carolina de la Torre 等
**摘要**:设计一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向CD89和肿瘤相关抗原,通过激活巨噬细胞吞噬作用及T细胞适应性免疫,显著抑制实体瘤模型中的肿瘤生长。
3. **文献名称**:*CD89 facilitates HIV-1 infection in myeloid cells through viral envelope interaction*
**作者**:Michael D. Valentin 等
**摘要**:揭示CD89通过与HIV-1包膜蛋白gp120结合,介导病毒进入单核/巨噬细胞,促进病毒潜伏库形成和免疫逃逸,为阻断感染提供新靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Genetic polymorphisms of CD89 correlate with susceptibility to autoimmune disorders*
**作者**:Anna B. Herr 等
**摘要**:通过全基因组关联分析,发现CD89基因特定单核苷酸多态性(SNPs)与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿性关节炎(RA)的易感性显著相关,提示其在自身免疫中的调控作用。
---
**注**:以上文献为模拟示例,基于CD89的典型研究方向(如炎症、肿瘤免疫、感染机制、遗传关联),实际文献需通过学术数据库检索。
CD89. also known as FcαRI (Fc alpha receptor I), is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on myeloid cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages. Discovered in the 1980s, it belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and binds the Fc region of immunoglobulin A (IgA), playing a pivotal role in mucosal immunity and inflammatory responses. Structurally, CD89 contains two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains that mediate IgA interaction, and its cytoplasmic tail triggers intracellular signaling upon ligand engagement.
CD89 bridges innate and adaptive immunity by facilitating IgA-mediated effector functions, including phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), and cytokine release. However, its dual role in immune regulation is notable: while CD89-IgA complexes can neutralize pathogens, excessive activation may contribute to inflammatory diseases like IgA nephropathy or rheumatoid arthritis. Dysregulated CD89 signaling has also been linked to autoimmune disorders and certain cancers.
Therapeutic interest in CD89 antibodies arises from their potential to modulate immune responses. Blocking CD89-IgA interactions could mitigate inflammation in autoimmune conditions, while CD89-targeting bispecific antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are being explored for cancer therapy. Recent studies focus on optimizing CD89 antibody specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Despite challenges, CD89 remains a promising target for treating IgA-mediated pathologies and enhancing immunotherapy strategies.
×