| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
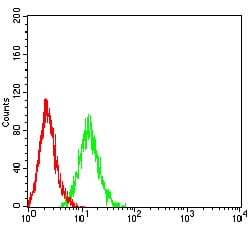
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
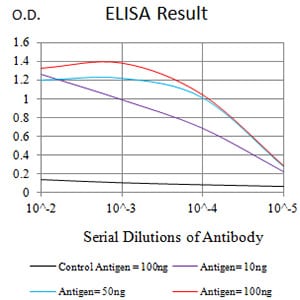
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BTLA1; CD272 |
| Entrez GeneID | 151888 |
| clone | 7H3E3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BTLA (AA: 179-289) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于BTLA抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **"BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1"**
- **作者**: Watanabe N, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究首次鉴定BTLA为T/B细胞共抑制受体,结构与CTLA-4和PD-1相似,通过结合HVEM抑制淋巴细胞激活,为靶向BTLA的抗体开发奠定理论基础。
2. **"BTLA mediates inhibition of human tumor-specific CD8+ T cells"**
- **作者**: Derré L, et al.
- **摘要**: 发现肿瘤浸润T细胞高表达BTLA,其信号抑制CD8+ T细胞抗肿瘤活性;使用抗BTLA抗体阻断可恢复T细胞功能,提示其作为免疫治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **"Anti-BTLA antibodies enhance T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity in combination with PD-1 blockade"**
- **作者**: Sordo-Bahamonde C, et al.
- **摘要**: 临床前研究表明,抗BTLA抗体与抗PD-1联用可协同增强T细胞活性,抑制小鼠肿瘤生长,支持BTLA与PD-1双靶向治疗的转化价值。
4. **"BTLA/HVEM axis in cancer immunotherapy: a systematic review"**
- **作者**: Severski J, et al.
- **摘要**: 综述总结BTLA-HVEM通路在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的作用,并分析抗BTLA抗体单用或联合治疗的临床前及早期临床数据,强调其安全性及疗效待验证。
(注:以上文献为领域内代表性研究方向示例,具体内容建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新原文确认。)
BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator) is a co-inhibitory receptor belonging to the CD28 immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on activated B cells, T cells, and antigen-presenting cells. Discovered in 2003. it shares structural and functional similarities with PD-1 and CTLA-4. playing a critical role in immune regulation. BTLA binds to its ligand HVEM (herpesvirus entry mediator), triggering inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. This interaction helps maintain immune homeostasis by preventing excessive inflammation and autoimmunity.
In cancer, BTLA is often upregulated in exhausted T cells within the tumor microenvironment, contributing to immune evasion. Targeting BTLA with blocking antibodies aims to disrupt its immunosuppressive signaling, thereby restoring anti-tumor immunity. Preclinical studies show synergistic effects when combining BTLA inhibitors with PD-1/CTLA-4 blockers. Conversely, in autoimmune disorders, enhancing BTLA signaling via agonist antibodies could theoretically suppress pathological immune responses, though this approach remains less explored.
Current research focuses on developing both antagonistic and agonistic BTLA antibodies. Early-phase clinical trials (e.g., anti-BTLA antibodies like icibrutimab) demonstrate preliminary safety and modulated immune activity in hematologic malignancies. Challenges include optimizing target specificity and understanding context-dependent roles of BTLA in different disease settings. As a relatively newer checkpoint, BTLA modulation represents a promising but underexplored avenue for precision immunotherapy.
×