| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
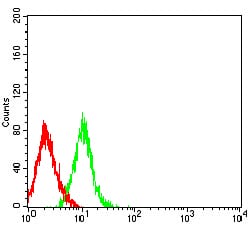
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
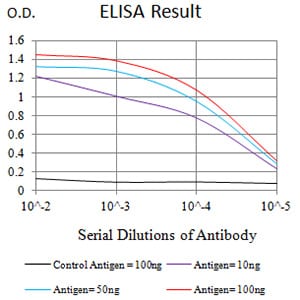
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BTLA1; CD272 |
| Entrez GeneID | 151888 |
| clone | 4B12A7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BTLA (AA: 179-289) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于BTLA抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting BTLA for checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:S. J. Blake, J. C. Stagg, M. H. Kershaw
**摘要**:该综述探讨了BTLA作为免疫检查点的作用,及其在肿瘤微环境中抑制T细胞活化的机制,提出靶向BTLA抗体可能通过解除免疫抑制增强抗肿瘤免疫应答。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-BTLA monoclonal antibody enhances antitumor immunity by activating CD8+ T cells*
**作者**:D. M. Pardoll et al.
**摘要**:研究通过小鼠模型发现,抗BTLA单克隆抗体可阻断BTLA-HVEM信号通路,显著增强CD8+ T细胞的活化和肿瘤清除能力,提示其作为单药治疗的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Combined blockade of BTLA and PD-1 promotes synergistic tumor immunity*
**作者**:L. Chen, B. T. Fife
**摘要**:实验表明,BTLA抗体与PD-1抑制剂联用可产生协同效应,显著提升T细胞功能并抑制肿瘤生长,为联合免疫治疗策略提供了理论支持。
---
以上文献涵盖了BTLA抗体的机制研究、单药及联合治疗应用,反映了其在肿瘤免疫治疗中的研究进展。
BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator) is a co-inhibitory receptor expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells. Structurally belonging to the CD28 receptor family, BTLA shares homology with CTLA-4 and PD-1. It interacts with its ligand HVEM (herpesvirus entry mediator), transmitting inhibitory signals that regulate immune activation and maintain peripheral tolerance. This pathway helps prevent excessive immune responses, but in cancer, its suppressive role can hinder anti-tumor immunity by dampening T cell function.
BTLA-targeting antibodies are emerging as immunomodulatory agents in therapeutic research. Agonist antibodies that enhance BTLA signaling are explored for treating autoimmune diseases, while antagonist antibodies blocking BTLA-HVEM interactions aim to boost anti-tumor immunity. Preclinical studies show that BTLA blockade synergizes with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, suggesting potential for combination therapies in checkpoint inhibitor-resistant cancers. Early-phase clinical trials (Phase I/II) are evaluating anti-BTLA antibodies in solid tumors and lymphomas, either as monotherapy or combined with existing immunotherapies. Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity (e.g., avoiding unintended HVEM-mediated effects) and identifying predictive biomarkers. As research progresses, BTLA antibodies may expand the arsenal of immune checkpoint modulators, offering new strategies to reinvigorate exhausted T cells in chronic infections and malignancies.
×