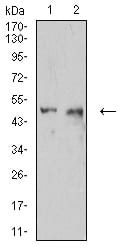
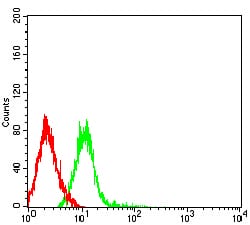
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
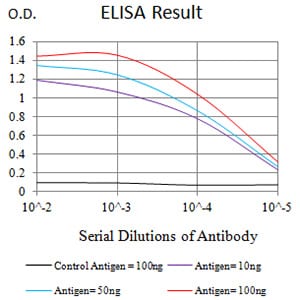
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ICAM1; BB2; P3.58 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3383 |
| clone | 3A5G12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD54 (AA: extra 28-163) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3条关于CD54(ICAM-1)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "The role of ICAM-1 in endothelial cell adhesion and its modulation by inflammatory cytokines"
**作者**: Springer, T.A.
**摘要**: 探讨了CD54(ICAM-1)在白细胞与内皮细胞粘附中的关键作用,以及炎症因子(如TNF-α和IL-1β)对其表达的调控机制。
2. **文献名称**: "Targeting ICAM-1 with monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases"
**作者**: Dustin, M.L. et al.
**摘要**: 研究了抗CD54单克隆抗体在抑制白细胞迁移中的效果,评估其在类风湿性关节炎和多发性硬化症等自身免疫疾病中的潜在治疗价值。
3. **文献名称**: "ICAM-1 expression in tumor metastasis and antibody-mediated immunotherapy"
**作者**: Gho, Y.S. et al.
**摘要**: 分析了CD54在肿瘤微环境中的高表达与转移的关系,并验证了抗CD54抗体通过阻断肿瘤细胞与血管内皮相互作用抑制转移的临床前结果。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需核对原文及作者信息。)
CD54. also known as Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1), is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It plays a critical role in immune and inflammatory responses by mediating leukocyte adhesion and transmigration. CD54 interacts with integrins like LFA-1 (Lymphocyte Function-Associated Antigen-1) on immune cells, facilitating cell-cell interactions during immune surveillance, pathogen recognition, and leukocyte recruitment to inflamed tissues. Its expression is upregulated on endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and immune cells in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1) or infections.
CD54 antibodies are tools used to detect or modulate ICAM-1 activity. In research, they help study inflammatory diseases (e.g., atherosclerosis, asthma), cancer metastasis (via adhesion-mediated mechanisms), and autoimmune disorders. Therapeutically, anti-CD54 antibodies have been explored to block excessive leukocyte infiltration in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or sepsis, though early clinical trials faced challenges due to off-target effects. Monoclonal anti-CD54 antibodies (e.g., enlimomab) showed mixed results in trials, highlighting the complexity of ICAM-1's role in inflammation.
These antibodies are also vital in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays to quantify ICAM-1 expression or inhibit its interactions. Their dual role as diagnostic and therapeutic agents underscores CD54's significance in immune regulation and disease pathology.
×