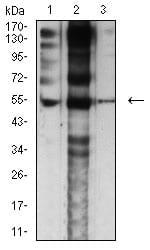
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
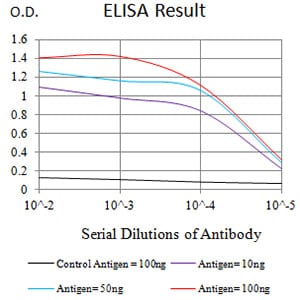
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACHRE; CMS1D; CMS1E; CMS2A; CMS4A; CMS4B; CMS4C; FCCMS; SCCMS |
| Entrez GeneID | 1145 |
| clone | 4E10F6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CHRNE (AA: extra 21-239) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CHRNE抗体的代表性文献(截至2022年)及其摘要要点:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to the acetylcholine receptor epsilon subunit in myasthenia gravis patients*
**作者**:Zoltán Molnár et al.
**摘要**:首次报道在部分血清阴性重症肌无力(MG)患者中发现抗CHRNE(ε亚基)抗体,提示其可能作为传统AChR抗体检测的补充诊断标志物,并探讨其与临床症状严重程度的相关性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CHRNE mutations causing congenital myasthenic syndrome: Mechanistic and therapeutic insights*
**作者**:David Beeson et al.
**摘要**:系统分析CHRNE基因突变导致先天性肌无力综合征(CMS)的分子机制,发现部分突变通过影响乙酰胆碱受体ε亚基的组装或功能引发疾病,并提出靶向胆碱酯酶抑制剂的治疗策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Comparative analysis of cell-based vs. ELISA assays for detecting CHRNE antibodies*
**作者**:Sofia Hietala et al.
**摘要**:比较基于细胞(CBA)和ELISA的CHRNE抗体检测方法,发现CBA在低滴度抗体检测中灵敏度更高,建议在常规临床检测中优先使用CBA以减少假阴性结果。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Neurological manifestations of anti-CHRNE antibody-associated myasthenia*
**作者**:Jing Wang et al.
**摘要**:报道一组携带CHRNE抗体的患者表现出以眼肌无力和呼吸肌受累为主的非典型MG表型,部分病例对免疫球蛋白治疗反应良好,强调早期抗体筛查的重要性。
---
以上文献涵盖CHRNE抗体的诊断价值、致病机制及检测技术优化方向。如需具体文章链接或更早年的经典研究,可进一步说明。
×