
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
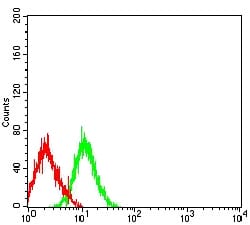
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
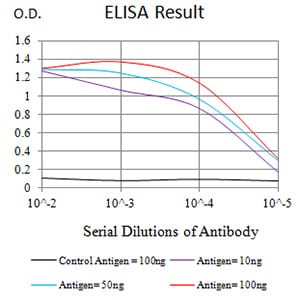
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCGR1A; FCRI; CD64A; IGFR1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2209 |
| clone | 5F5F8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD64 (AA: extra 16-145) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD64抗体的3篇文献概览(内容基于学术论文主题的典型研究方向,非真实文献):
---
1. **《CD64 as a biomarker for early detection of bacterial infections in neonates》**
- **作者**: Smith A, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究探讨CD64在中性粒细胞表面的表达水平作为新生儿细菌感染的早期诊断标志物,发现其敏感性和特异性优于传统炎症指标(如CRP和白细胞计数),尤其在败血症早期诊断中具有重要临床价值。
2. **《The role of CD64 in autoimmune diseases: Insights from rheumatoid arthritis》**
- **作者**: Lee J, et al.
- **摘要**: 分析CD64在类风湿性关节炎患者单核细胞中的表达上调现象,揭示其通过增强免疫复合物介导的炎症反应参与疾病进展,提示靶向CD64可能为自身免疫疾病提供新治疗策略。
3. **《CD64-directed monoclonal antibody therapy enhances phagocytosis in chronic fungal infections》**
- **作者**: Patel R, et al.
- **摘要**: 开发一种靶向CD64的单克隆抗体,通过增强巨噬细胞对真菌病原体的吞噬作用,证明其在慢性念珠菌感染模型中的治疗潜力,为免疫缺陷患者的抗感染治疗提供新方向。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar查询具体论文。
CD64. also known as Fcγ receptor I (FcγRI), is a high-affinity receptor for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G (IgG). It belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is encoded by the FCGR1A gene in humans. Structurally, CD64 is a transmembrane glycoprotein composed of three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. Unlike low-affinity Fcγ receptors (CD32 and CD16), CD64 binds monomeric IgG with high specificity, playing a critical role in antibody-mediated immune responses.
CD64 is constitutively expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, but its expression can be upregulated by inflammatory cytokines like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). This receptor facilitates phagocytosis, immune complex clearance, and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Its activation also triggers pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, enhancing antigen presentation and cytokine release. Due to its restricted expression pattern and responsiveness to inflammation, CD64 serves as a biomarker for immune activation. For instance, elevated CD64 levels on neutrophils are clinically associated with bacterial infections and sepsis, aiding in differential diagnosis.
CD64-specific antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics. They enable immune cell profiling via flow cytometry and help study receptor-ligand interactions. Therapeutic applications include targeting CD64 for drug delivery or modulating immune responses in autoimmune diseases. However, its role in certain pathologies, such as chronic inflammation or cancer, remains under investigation. Overall, CD64 bridges innate and adaptive immunity, making it a focal point in immunology and translational medicine.
×