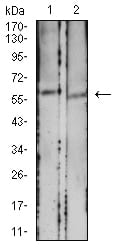
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
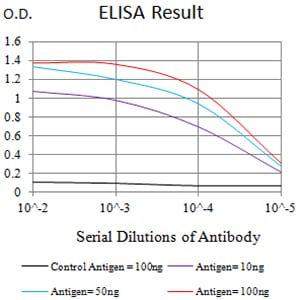
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ENTPD1; SPG64; ATPDase; NTPDase-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 953 |
| clone | 8E9F2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 58kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD39 (AA: extra 38-179) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD39抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "CD39 Antibody Blocks Adenosine Suppression in the Tumor Microenvironment"
**作者**: Allard B. et al.
**摘要**: 研究证明抗CD39单克隆抗体可抑制肿瘤微环境中CD39介导的ATP水解,减少免疫抑制性腺苷积累,增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,为联合免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**: "Targeting CD39 in Cancer Reveals Dual Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition"
**作者**: Perrot I. et al.
**摘要**: 通过临床前模型发现,CD39抗体不仅阻断腺苷生成,同时维持细胞外ATP水平以激活促炎反应,双重机制增强抗PD-1疗法的协同效应。
3. **文献名称**: "Anti-CD39 Antibody Prevents Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Sepsis"
**作者**: Killeen M.E. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示CD39抗体通过调节嘌呤代谢,减少脓毒症模型中中性粒细胞胞外陷阱(NETs)的形成,改善全身炎症反应,提示其在败血症治疗中的潜力。
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实具体来源及发表年份。
CD39. also known as ENTPD1. is a cell surface ectonucleotidase that hydrolyzes extracellular ATP and ADP into AMP, a critical step in the purinergic signaling pathway. AMP is further converted by CD73 into immunosuppressive adenosine, which binds to adenosine receptors (e.g., A2A) to dampen immune responses. CD39 is expressed on regulatory T cells (Tregs), exhausted T cells, and tumor-infiltrating immune cells, playing a key role in maintaining immune tolerance and shaping the tumor microenvironment. Its upregulation in cancers and chronic inflammatory diseases correlates with immune evasion and poor prognosis, making it a promising therapeutic target.
CD39-blocking antibodies aim to disrupt this immunosuppressive pathway by inhibiting ATP/ADP hydrolysis, thereby reducing adenosine accumulation while preserving pro-inflammatory extracellular ATP. Preclinical studies show that targeting CD39 enhances anti-tumor immunity by reactivating effector T cells and reducing Treg-mediated suppression. These antibodies are being explored in cancer immunotherapy, either as monotherapy or in combination with checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1). Several CD39-targeting antibodies, such as SRF617 (Surface Oncology) and AZD8701 (AstraZeneca), are in Phase I/II trials for solid tumors.
Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity to avoid off-target effects and balancing therapeutic efficacy with potential toxicity from systemic immune activation. Emerging strategies focus on selective epitope targeting or Fc-engineered antibodies to modulate cellular interactions. Additionally, CD39 expression levels are being investigated as a predictive biomarker for patient stratification. Overall, CD39 antibodies represent a novel approach to reprogram the tumor microenvironment and overcome resistance to existing immunotherapies.
×