| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
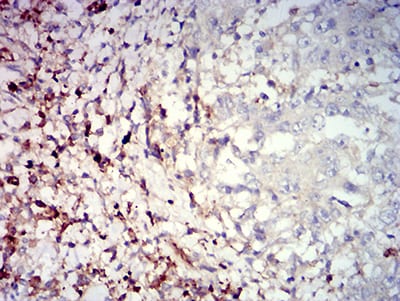
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
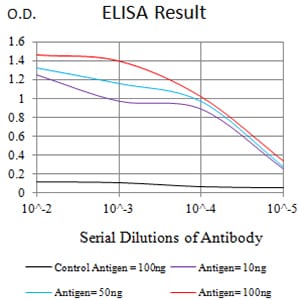
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ENTPD1; SPG64; ATPDase; NTPDase-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 953 |
| clone | 6H12F9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 58kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD39 (AA: extra 38-179) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD39抗体的代表性文献,涵盖机制研究及治疗应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD39 is a critical regulator of T cell suppression in the tumor microenvironment*
**作者**:Allard B. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示CD39通过水解细胞外ATP,在肿瘤微环境中抑制T细胞功能并促进免疫逃逸,阻断CD39可增强抗肿瘤免疫反应。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-CD39 antibody potentiates anti-tumor immunity by disrupting the immunosuppressive adenosine axis*
**作者**:Perrot I. et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种新型CD39抗体,可在临床前模型中有效抑制腺苷生成,增强T细胞活性,并与PD-1抑制剂协同抑制肿瘤生长。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD39 in cancer reveals an extracellular ATP-driven immunosuppressive pathway*
**作者**:Moesta A.K. et al.
**摘要**:通过基因敲除和抗体阻断实验,证实靶向CD39可逆转ATP-腺苷转化介导的免疫抑制,为联合免疫治疗提供理论依据。
---
如需更多文献或特定研究方向的推荐,可进一步说明需求。
CD39. also known as ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (ENTPD1), is a cell membrane-bound enzyme that plays a key role in purinergic signaling by hydrolyzing extracellular ATP and ADP into AMP. This process ultimately leads to the generation of immunosuppressive adenosine via the sequential activity of CD73. CD39 is expressed on various immune cells, including regulatory T cells (Tregs), dendritic cells, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, as well as certain cancer cells. Its enzymatic activity contributes to the establishment of an immunosuppressive microenvironment, particularly in tumors, by dampening pro-inflammatory ATP signaling and promoting adenosine-mediated immune suppression.
CD39 antibodies are investigative tools and therapeutic agents designed to target this pathway. By blocking CD39’s enzymatic function, these antibodies aim to reduce adenosine accumulation, enhance ATP-driven pro-inflammatory responses, and counteract immune evasion in diseases like cancer. Preclinical studies suggest that CD39 inhibition can synergize with other immunotherapies, such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents, to improve antitumor immunity. Additionally, CD39 antibodies are explored for modulating autoimmune and inflammatory conditions where purinergic signaling dysregulation is implicated. Research continues to clarify their dual role in either agonizing or antagonizing CD39 activity, depending on antibody specificity and disease context. Current efforts focus on optimizing antibody design and evaluating clinical efficacy in ongoing trials.
×