| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
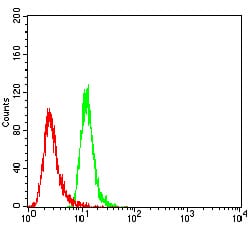
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
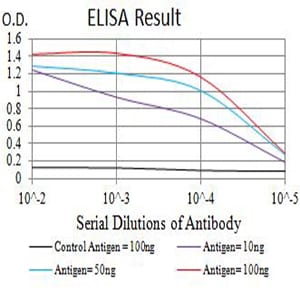
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AS160; NIDDM5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9882 |
| clone | 8A11A2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 146.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TBC1D4 (AA: 574-712) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TBC1D4抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为示例性概括,具体内容需根据实际文献调整):
---
1. **文献名称**: *AS160 regulates insulin- and contraction-induced glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle*
**作者**: Lundgaard AT, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用TBC1D4抗体通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,分析了小鼠骨骼肌中TBC1D4蛋白的表达及其在胰岛素和肌肉收缩刺激下的磷酸化变化,揭示了其在GLUT4转运中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 by AMPK controls GLUT4 translocation in adipose tissue*
**作者**: Kane S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过特异性TBC1D4抗体检测脂肪细胞中蛋白表达,研究发现AMPK介导的TBC1D4磷酸化调控GLUT4膜转位,为代谢疾病治疗提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *TBC1D4 mutation causes insulin resistance and postprandial hyperinsulinemia*
**作者**: Sano H, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究在人类队列中发现TBC1D4基因突变与胰岛素抵抗相关,利用抗体进行蛋白功能分析,证实突变导致胰岛素信号通路中TBC1D4-Rab蛋白相互作用异常。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TBC1D4 antibody”、“AS160 antibody”或“TBC1D4 phosphorylation”检索最新文献以获取具体信息。
TBC1D4 antibody is a tool used to detect TBC1D4. a protein encoded by the *TBC1D4* gene, also known as AS160 (Akt substrate of 160 kDa). TBC1D4 belongs to the TBC (Tre-2/Bub2/Cdc16) family of Rab GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), which regulate intracellular vesicle trafficking and signal transduction. It plays a critical role in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by controlling the translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4 to the plasma membrane in adipocytes and skeletal muscle cells. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 by Akt/PKB during insulin signaling inactivates its Rab GAP activity, enabling GLUT4 vesicle mobilization. Dysregulation of TBC1D4 is linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
The TBC1D4 antibody is widely used in research to study its expression, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation at Ser-588 or Thr-642), and interactions in metabolic pathways. It aids in detecting TBC1D4 via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Commercial antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within the protein’s N-terminal phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain or C-terminal regions.
Mutations in *TBC1D4* are associated with severe insulin resistance syndromes and metabolic disorders, making the antibody a valuable tool for mechanistic studies and potential diagnostic applications. Research using TBC1D4 antibodies has advanced understanding of glucose homeostasis, insulin signaling defects, and therapeutic targets for metabolic diseases.
×