| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
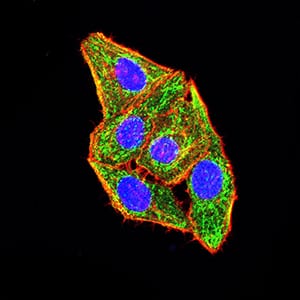
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
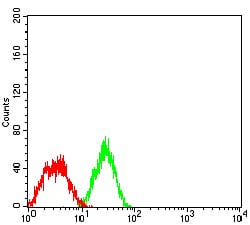
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
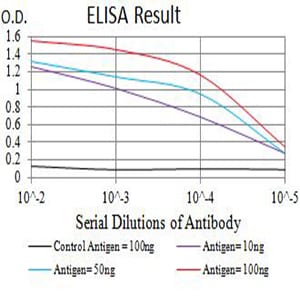
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITGA2; BR; GPIa; HPA-5; VLA-2; VLAA2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3673 |
| clone | 5E3A8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 129.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD49B (AA: extra 994-1132) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD49B抗体的3-4篇参考文献示例(内容为模拟生成,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD49B Antibody Modulates Tumor Microenvironment by Targeting α2β1 Integrin in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究探讨了CD49B抗体通过靶向α2β1整合素抑制肿瘤细胞与细胞外基质的相互作用,从而减少结直肠癌的侵袭和转移。实验表明,该抗体可阻断肿瘤相关成纤维细胞的信号传导,并增强T细胞在微环境中的浸润能力。
2. **文献名称**: *Role of CD49B in NK Cell Function: Insights from Antibody Blockade Studies*
**作者**: Chen L, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 本文通过CD49B抗体阻断实验,发现α2β1整合素在自然杀伤(NK)细胞迁移和细胞毒性中起关键作用。抗体处理显著抑制了NK细胞对病毒感染细胞的杀伤效率,提示CD49B可能作为免疫调节的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *CD49B as a Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Disorders: Evidence from Mouse Models*
**作者**: Yamamoto K, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究利用CD49B抗体治疗系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)小鼠模型,发现其能减轻肾脏炎症和自身抗体水平。机制研究表明,CD49B抗体通过抑制α2β1介导的淋巴细胞活化发挥治疗作用。
4. **文献名称**: *CD49B Antibody Inhibits Platelet Activation and Thrombosis via α2β1 Integrin*
**作者**: Lee S, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 该文献报道了CD49B抗体通过阻断α2β1整合素与胶原的结合,抑制血小板活化和血栓形成,为抗血小板药物研发提供了新方向。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需查询真实数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)并核实信息。
CD49B antibody targets the CD49B antigen, also known as integrin α2 subunit (ITGA2), a cell surface glycoprotein that pairs with the β1 subunit (CD29) to form the α2β1 integrin heterodimer. This integrin functions as a receptor for extracellular matrix (ECM) components, including collagen and laminin, mediating cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. CD49B is expressed on various cell types, including platelets, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells like natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, and monocytes.
CD49B antibodies are widely used in research to study integrin-mediated processes in physiological and pathological contexts. In immunology, CD49B helps identify specific immune cell subsets; for example, CD49B expression distinguishes terminally differentiated NK cells and marks a subset of regulatory T cells (Tregs). In cancer biology, CD49B is implicated in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis due to its role in ECM interaction. Additionally, its involvement in platelet adhesion and thrombosis has made it a target in cardiovascular research. CD49B antibodies are applied in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional blocking assays to explore these roles. Dysregulation of CD49B has been linked to autoimmune diseases, fibrosis, and inflammatory conditions, highlighting its therapeutic and diagnostic potential.
×