| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
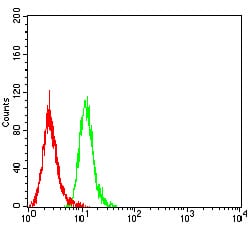
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
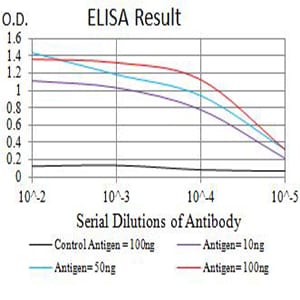
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p50; Bp50; CDW40; TNFRSF5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 958 |
| clone | 4C3B8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD40 (AA: extra 21-193) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD40抗体的代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD40 Agonism Enhances Checkpoint Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer*
**作者**: Vonderheide, R.H. 等 (2020)
**摘要**: 该研究评估了CD40激动型抗体(如APX005M)联合PD-1抑制剂在胰腺癌治疗中的作用。结果显示,CD40激活可增强肿瘤微环境中T细胞浸润,并与免疫检查点抑制剂产生协同抗肿瘤效应,显著延长临床前模型生存期。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting CD40 in Cancer: From Biology to Therapy*
**作者**: Melero, I. & Haanen, J.B. (2018)
**摘要**: 综述了CD40信号在抗肿瘤免疫中的双重作用(激活抗原呈递细胞 vs. 促炎风险),总结了CD40抗体(激动型/拮抗型)的临床前及临床试验进展,并探讨其与化疗、放疗及免疫疗法的联合策略。
---
3. **文献名称**: *CD40 Antibodies as Vaccine Adjuvants: Preclinical and Clinical Insights*
**作者**: Diehl, L. 等 (2019)
**摘要**: 研究证明CD40激动型抗体可通过激活树突状细胞增强疫苗诱导的抗原特异性T细胞应答,在HIV和肿瘤疫苗模型中显著提升保护效果,同时讨论了优化给药时机以平衡疗效与细胞因子风暴风险的策略。
---
**可选补充**
4. **文献名称**: *CD40L Blockade in Autoimmune Disease: Mechanisms and Outcomes*
**作者**: Pieper, K. 等 (2021)
**摘要**: 探讨拮抗型CD40/CD40L抗体(如Iscalimab)在类风湿性关节炎和系统性红斑狼疮中的治疗潜力,显示其通过抑制B细胞过度活化及自身抗体产生缓解疾病活动度,但需警惕血栓形成风险。
---
以上文献覆盖了CD40抗体在癌症免疫治疗、疫苗佐剂开发及自身免疫疾病干预中的关键机制与应用。
CD40. a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, is expressed on immune cells such as B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Its interaction with CD40 ligand (CD40L/CD154) on T cells plays a critical role in adaptive immunity, including B-cell activation, antibody class switching, and dendritic cell maturation. Dysregulation of CD40 signaling is implicated in cancers, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation, making it a therapeutic target.
CD40-targeting antibodies are designed to modulate this pathway. Agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies (e.g., APX005M, SEA-CD40) activate CD40 signaling, mimicking CD40L to enhance antigen-presenting cell function and boost antitumor immune responses. These are explored in cancer immunotherapy, often combined with checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy. Conversely, antagonistic anti-CD40 antibodies (e.g., dacetizumab) block CD40-CD40L interactions, suppressing pathogenic immune activity in autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Structurally, CD40 antibodies vary in isotype (IgG1. IgG2) and epitope specificity, influencing their functional outcomes (e.g., Fc receptor engagement, immune cell recruitment). Challenges include balancing efficacy with toxicity, as systemic CD40 activation can trigger cytokine release or liver inflammation. Current research focuses on optimizing dosing, tumor-targeted delivery, and combination regimens to maximize therapeutic benefits. Clinical trials highlight their potential in reshaping immune responses across oncology and autoimmunity.
×