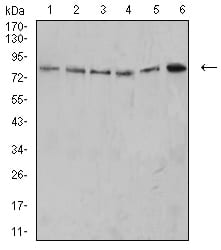
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
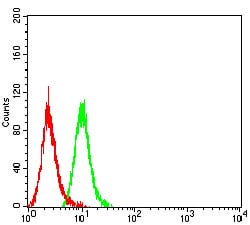
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
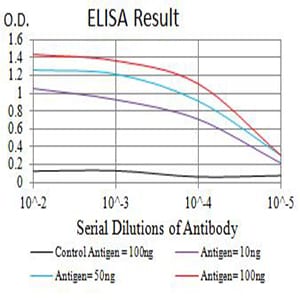
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PDCD1; PD-1; CD279; SLEB2; hPD-1; hPD-l; hSLE1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5133 |
| clone | 1D6F6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.6KD |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PD1 (AA: extra 21-170) expressed in HEK293 cells. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PD-1抗体的重要文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*Safety and Activity of Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Advanced Melanoma*
**作者**:Topalian SL等(2012)
**摘要**:首次报道抗PD-1抗体nivolumab在晚期黑色素瘤中的I期临床试验结果,显示客观缓解率约28%,且毒性可控,奠定了PD-1抗体在实体瘤中的治疗潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer*
**作者**:Garon EB等(2015.KEYNOTE-001试验)
**摘要**:证实pembrolizumab在PD-L1高表达晚期非小细胞肺癌患者中的显著疗效(客观缓解率19.4%),推动PD-L1作为生物标志物的临床应用。
3. **文献名称**:*PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma*
**作者**:Ansell SM等(2015)
**摘要**:在自体干细胞移植失败的经典霍奇金淋巴瘤患者中,nivolumab达到87%的客观缓解率,凸显PD-1抗体在血液肿瘤中的突破性效果。
*注*:若需扩展,可补充2018年Sharpe等发表于*Nature Reviews Immunology*的综述,系统解析PD-1通路机制及临床转化进展。
**Background of PD-1 Antibodies**
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on activated T cells, playing a critical role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity. Tumors often exploit the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway to evade immune surveillance by binding PD-1 to its ligands (PD-L1/PD-L2), thereby suppressing T-cell activation and promoting an immunosuppressive microenvironment.
PD-1 antibodies, a class of immune checkpoint inhibitors, block this interaction, restoring T-cell-mediated antitumor responses. The first PD-1 antibody, nivolumab, was approved in 2014. followed by pembrolizumab. These drugs revolutionized cancer treatment, showing remarkable efficacy in melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other malignancies. Their development stemmed from decades of research into T-cell regulation and immune evasion mechanisms.
Clinically, PD-1 antibodies are notable for durable responses and improved survival in advanced cancers. However, response variability and immune-related adverse events (e.g., colitis, pneumonitis) remain challenges. Ongoing research focuses on combination therapies (e.g., with chemotherapy, CTLA-4 inhibitors) and biomarkers (e.g., PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden) to optimize outcomes. PD-1 antibodies exemplify the shift toward precision immunotherapy, highlighting the interplay between immune biology and therapeutic innovation.
×