| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
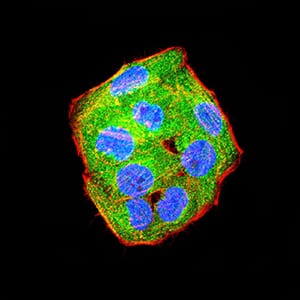
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
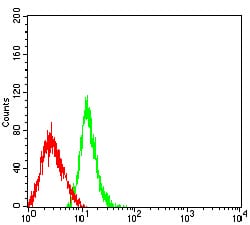
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
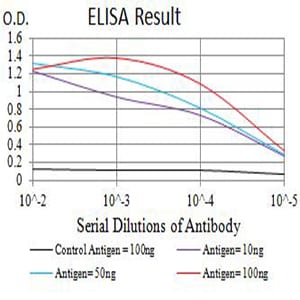
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PDCD1; PD-1; CD279; SLEB2; hPD-1; hPD-l; hSLE1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5133 |
| clone | 3E12A10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.6KD |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PD1 (AA: extra 21-170) expressed in HEK293 cells. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PD-1抗体的经典文献摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer
**作者**:Topalian SL, et al.
**摘要**:该研究发表于《新英格兰医学杂志》(2012),首次报道了PD-1抗体(nivolumab)在晚期黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌等实体瘤中的I期临床试验结果。结果显示,患者总体客观缓解率为18-28%,且治疗耐受性良好,验证了PD-1抗体通过阻断免疫检查点激活T细胞的抗肿瘤潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma
**作者**:Robert C, et al.
**摘要**:发表于《新英格兰医学杂志》(2015)的III期临床试验(KEYNOTE-006),比较PD-1抗体(pembrolizumab)与CTLA-4抗体(ipilimumab)在晚期黑色素瘤中的疗效。结果显示,pembrolizumab组患者的6个月无进展生存率和总生存率显著优于ipilimumab组,且不良反应更低,确立了PD-1抗体作为一线治疗的优势。
---
3. **文献名称**:Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in Untreated Melanoma
**作者**:Wolchok JD, et al.
**摘要**:该研究(CheckMate 067试验,发表于《新英格兰医学杂志》2017年)评估PD-1抗体(nivolumab)联合CTLA-4抗体(ipilimumab)治疗晚期黑色素瘤的效果。联合治疗组患者的中位无进展生存期显著延长(11.5个月 vs 单药6.9个月),但毒性反应增加,提示需权衡疗效与安全性。
---
4. **文献名称**:PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
**作者**:Ansell SM, et al.
**摘要**:发表于《新英格兰医学杂志》(2015)的I期研究,首次证明PD-1抗体(nivolumab)在复发/难治性霍奇金淋巴瘤中的显著疗效。客观缓解率达87%,且多数患者肿瘤缩小,揭示了PD-1抗体在血液肿瘤中的临床应用潜力。
---
这些研究涵盖了PD-1抗体在实体瘤、血液肿瘤中的单药及联合治疗数据,反映了其在癌症免疫治疗中的里程碑意义。
PD1 (Programmed Death-1) is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on activated T cells, playing a critical role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity. It interacts with ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 on antigen-presenting cells or tumor cells, transmitting inhibitory signals that suppress T-cell activation and promote exhaustion. Tumors often exploit this pathway by upregulating PD-L1 to evade immune surveillance.
The development of PD1-blocking antibodies marked a breakthrough in cancer immunotherapy. The first anti-PD1 antibodies, nivolumab and pembrolizumab, were approved in 2014 after demonstrating unprecedented efficacy in advanced melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. These antibodies disrupt PD1/PD-L1 interactions, revitalizing exhausted T cells to attack tumors. Their success validated the concept of immune checkpoint inhibition, shifting treatment paradigms toward harnessing the body’s immune system rather than directly targeting cancer cells.
PD1 antibodies now form the backbone of therapy for multiple malignancies, including renal cell carcinoma and Hodgkin’s lymphoma, often achieving durable responses. Combination strategies with CTLA-4 inhibitors, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies further enhance efficacy. However, challenges persist, such as variable response rates, immune-related adverse events, and acquired resistance. Ongoing research focuses on predictive biomarkers (e.g., PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden) and novel combinatorial approaches to expand clinical benefits while managing toxicity. PD1 antibodies exemplify the translation of fundamental immunology into transformative cancer treatments.
(Word count: 249)
×