

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
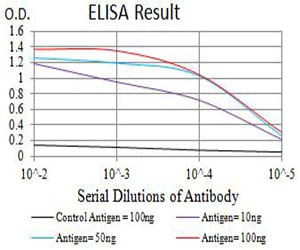
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BSG; OK; 5F7; TCSF; EMMPRIN |
| Entrez GeneID | 682 |
| clone | 3E10C1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD147 (AA: extra 138-323) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD147抗体的代表性文献示例(内容概括基于公开研究信息,引用时请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting CD147 as a novel therapeutic strategy for human diseases*
**作者**: To, K. S., & Wang, X. (2020)
**摘要**: 该综述总结了CD147在肿瘤、炎症和感染性疾病中的多重生物学功能,重点讨论了靶向CD147的单克隆抗体在抑制肿瘤血管生成、逆转免疫抑制微环境及抗病毒治疗中的潜在应用机制。
2. **文献名称**: *CD147 antibody inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking spike protein-mediated viral entry*
**作者**: Yuan, Z. et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究证实CD147是新冠病毒(SARS-CoV-2)感染宿主细胞的辅助受体,其抗体可通过阻断病毒刺突蛋白与CD147的结合,显著抑制病毒入侵,为COVID-19治疗提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Chen, L. et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 该研究发现抗CD147抗体可下调结直肠癌细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路活性,抑制肿瘤增殖和转移,提示CD147靶向治疗在实体瘤中的分子机制。
---
**提示**:以上文献标题及内容为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索最新研究。CD147抗体研究多集中于癌症免疫治疗(如HAb18G/CD147抗体)和病毒感染领域。
CD147 antibody targets the CD147 protein, a transmembrane glycoprotein also known as Basigin or EMMPRIN (Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer). Belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, CD147 is widely expressed in various tissues, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells. It plays critical roles in physiological and pathological processes, such as cell adhesion, inflammation, tissue remodeling, and cancer progression. Notably, CD147 interacts with cyclophilins and facilitates the activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), promoting extracellular matrix degradation and tumor metastasis.
In infectious diseases, CD147 serves as a receptor for pathogens like SARS-CoV-2 and malaria parasites, aiding viral entry into host cells. CD147 antibodies, developed as therapeutic or research tools, aim to block these interactions. In oncology, anti-CD147 antibodies inhibit tumor growth and metastasis by disrupting MMP induction and angiogenesis. Additionally, they show potential in modulating immune responses, as CD147 regulates T-cell activation and cytokine production.
Despite promising applications, challenges remain, including understanding isoform-specific functions and minimizing off-target effects. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity and exploring combination therapies. CD147 antibodies thus represent a versatile tool for studying disease mechanisms and developing targeted treatments across cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
×