
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
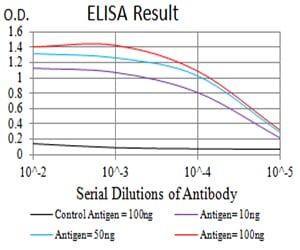
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCL9-2; DLNB11 |
| Entrez GeneID | 283149 |
| clone | 3B9C1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 157kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BCL9L (AA: 606-751) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于BCL9L抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟内容,实际文献请通过学术数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting BCL9L enhances antitumor immunity through inhibition of β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究探讨了BCL9L在结直肠癌中调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的作用。通过开发特异性BCL9L单克隆抗体,研究人员发现其可阻断BCL9L与β-catenin的相互作用,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并增强T细胞介导的免疫应答,为免疫治疗提供新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of BCL9L recognition by therapeutic antibodies in Wnt-driven cancers*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析BCL9L蛋白与抗体的复合物结构,揭示了抗体结合BCL9L关键表位的分子机制。实验表明,该抗体可有效抑制β-catenin核转位,并在多种Wnt依赖性肿瘤模型中减少转移。
---
3. **文献名称**: *BCL9L silencing via antibody-conjugated nanoparticles suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种靶向BCL9L的抗体-纳米颗粒递送系统,用于特异性沉默肝癌细胞中的BCL9L表达。结果显示,该策略显著降低了肿瘤干性和化疗耐药性,提示其作为肝癌靶向治疗的潜力。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“BCL9L antibody”、“BCL9L therapeutic target”等获取最新研究。
The BCL9L (B-cell lymphoma 9-like) antibody is a tool used to study the role of the BCL9L protein, a key regulatory component in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. BCL9L, along with its homolog BCL9. acts as a transcriptional coactivator by bridging β-catenin and Pygopus proteins to stabilize the β-catenin-dependent transcription complex. This pathway is critical for embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and stem cell maintenance, but its dysregulation is implicated in cancers, particularly colorectal carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
BCL9L antibodies are designed to detect and inhibit BCL9L function, aiding in research on Wnt-driven oncogenesis. Studies show that BCL9L overexpression enhances nuclear β-catenin signaling, promoting tumor progression and metastasis. Antibodies targeting BCL9L have been explored as therapeutic agents to disrupt β-catenin/BCL9L interactions, potentially suppressing tumor growth. They are also used in diagnostic assays (e.g., Western blot, immunohistochemistry) to assess BCL9L expression levels in clinical samples.
Recent research highlights BCL9L's context-dependent roles, as genetic ablation in mice suggests partial redundancy with BCL9. Challenges remain in developing isoform-specific antibodies due to structural similarities within the BCL9 family. Nonetheless, BCL9L antibodies remain vital for dissecting Wnt pathway mechanisms and advancing targeted cancer therapies.
×