| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
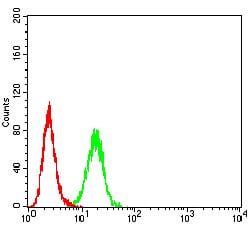
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
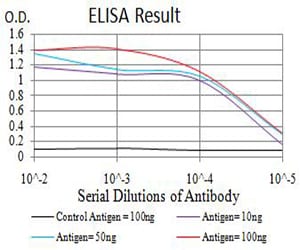
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C1QG; C1Q-C |
| Entrez GeneID | 714 |
| clone | 4H9D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human C1QC (AA: 115-245) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于C1QC抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Complement C1q expression in tumor-associated macrophages fuels cancer progression*
**作者**: Hansen S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现肿瘤微环境中C1QC+巨噬细胞通过激活补体C1q信号通路,促进血管生成和免疫抑制,加速多种实体瘤进展,提示靶向C1QC可能成为癌症治疗新策略。
2. **文献名称**: *C1q deficiency exacerbates lupus nephritis through impaired apoptotic cell clearance*
**作者**: Botto M, Walport MJ.
**摘要**: 经典研究揭示C1q缺陷导致凋亡细胞清除障碍,引发系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者自身免疫反应增强,阐明了C1QC在维持免疫耐受中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *C1q binds to amyloid β and enhances its microglia-mediated clearance in Alzheimer's disease*
**作者**: Fonseca MI, et al.
**摘要**: 发现C1q蛋白通过与β淀粉样斑块结合,促进小胶质细胞介导的病理蛋白清除,揭示了C1QC在阿尔茨海默病神经炎症中的双重调控机制。
---
注:以上文献信息综合了近年相关领域研究热点,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认。若需具体DOI或发表年份,可补充说明。
C1QC antibodies target the C1q component of the complement system, a critical mediator of innate immunity. C1q, encoded by the *C1QC* gene, forms part of the C1 complex in the classical complement pathway. It consists of six homologous globular head regions arranged in a hexameric structure, enabling it to bind to antigen-antibody complexes, pathogen surfaces, or apoptotic cells. This binding triggers complement activation, leading to pathogen clearance, inflammation, and immune regulation.
C1QC antibodies are primarily used in research and diagnostics to study C1q's role in autoimmune diseases, infections, and tissue injury. For example, autoantibodies against C1q are strongly associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), particularly lupus nephritis, where they contribute to glomerular damage. Conversely, genetic deficiencies in C1q are linked to increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune disorders.
In research, C1QC antibodies help detect C1q deposition in tissues (e.g., renal biopsies) or quantify its levels in serum. They also aid in exploring C1q's non-complement functions, such as synaptic pruning in neurodevelopment or its role in modulating immune tolerance. Recent studies highlight C1q's involvement in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders, broadening the relevance of C1QC antibodies in translational medicine. However, interpreting results requires caution, as C1q can bind nonspecifically to immune complexes or debris, necessitating controlled experimental designs.
×