| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
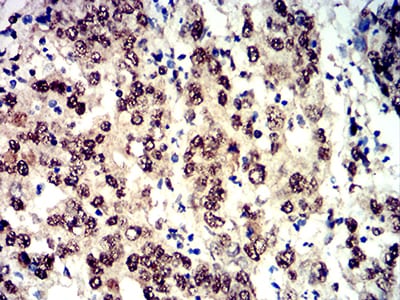
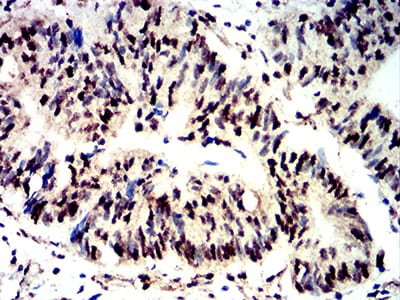
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
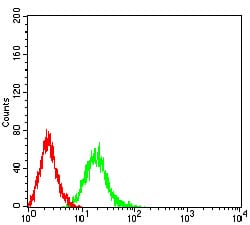
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
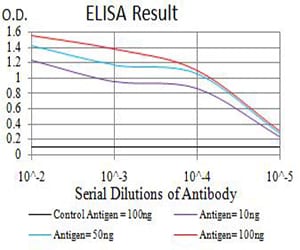
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EIF4EBP1; BP-1; 4EBP1; 4E-BP1; PHAS-I |
| Entrez GeneID | 1978 |
| clone | 2D1G11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 12.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65)抗体的参考文献(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **"Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation by mTOR and PP2A in cell growth control"**
作者:Gingras AC, et al.
摘要:研究揭示了mTOR信号通过调控4E-BP1的Ser65磷酸化促进蛋白质翻译,Western blot中使用Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65)抗体验证了氨基酸剥夺对磷酸化水平的影响。
2. **"Amino acid signalling upstream of mTOR"**
作者:Hara K, et al.
摘要:探讨氨基酸如何通过mTORC1调控4E-BP1磷酸化,实验通过Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65)抗体检测到Ser65位点的磷酸化状态与细胞营养状态直接相关。
3. **"Therapeutic targeting of mTOR-dependent translation in cancer"**
作者:Choo AY, et al.
摘要:研究评估mTOR抑制剂对肿瘤细胞的影响,利用Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65)抗体证明药物处理后Ser65磷酸化水平下降,提示翻译抑制效应。
4. **"Rapamycin inhibits mTORC1. but not completely"**
作者:Thoreen CC, et al.
摘要:发现雷帕霉素仅部分阻断mTORC1活性,通过Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65)抗体观察到残余Ser65磷酸化维持了部分蛋白质合成能力。
---
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需以具体论文数据为准。)
The Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65) antibody detects the phosphorylated form of 4E-BP1 (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1) at serine 65. a key regulatory site in the mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) signaling pathway. 4E-BP1 acts as a suppressor of cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E), preventing the assembly of the translation initiation complex. Upon activation of mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1) by growth factors, nutrients, or cellular stress, 4E-BP1 undergoes hierarchical phosphorylation at multiple residues, including Ser65. This phosphorylation disrupts its interaction with eIF4E, enabling the initiation of protein synthesis critical for cell growth, proliferation, and survival.
The Phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65) antibody is widely used in research to study mTOR pathway activity, particularly in contexts such as cancer, metabolic disorders, and aging. Elevated phosphorylation at Ser65 is often associated with hyperactive mTOR signaling, a hallmark of many tumors. Researchers employ this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry to assess phosphorylation status in cell lines, tissues, or preclinical models. Specificity is validated using controls such as phosphatase-treated samples or genetic knockouts. Its application helps elucidate therapeutic responses to mTOR inhibitors (e.g., rapamycin) and contributes to biomarker discovery in diseases linked to dysregulated translation control. Proper experimental design requires parallel assessment of total 4E-BP1 levels to confirm phosphorylation-specific changes.
×